Figure 3.
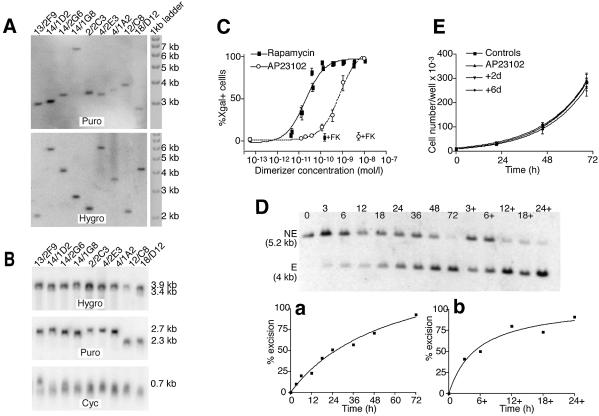
Analysis of DiCre expressing stable Rat2/CALNLZ transformants. (A) Southern blot analysis of the integration for the Cre constructs in clones displaying different levels of background activity. The background values (percentage of X-gal+ cells in the absence of dimerizer) for the clones are 59(F2)/60(F5) clones: 13/2F9, 0.1%; 14/1D2, 0.1%; 14/2G6, 0.4%; 14/1G8, 0.05%; 104.F6–106.F6 clone 2/2C3, 25.1; 104.F5–106.F5 clones, 4/2E3, 3.1%; 4/1A2, 36%; 59/60 clone 12/C8, 0.7 %; 104/106 clone 18/D12, 100%. To analyze the 59(F2), 104(F5), 104(F6), Cre(59) and Cre(104) constructs, hybridization was performed with a probe homologous to a 760 bp sequence of the puromycin (Puro) resistance gene of the pQCXIP bicistronic vector, while for the 60(F2), 106(F5), 106(F6), Cre(60) and Cre(106) constructs, an RNA probe of 1030 nucleotides, homologous to the hygromycin (Hygro) resistance gene of the pQCXIH bicistronic vector, was used. For each clone, a single band, indicative of a single insertion, was obtained for both constructs. (B) Northern blot analysis of the level of transcription of the transduced Cre construct in the clones analyzed in (A). The same probes were used as in (A) with an additional 630 bp probe homologous to cyclophilin A (Cyc). The differences in mRNA levels found between the different clones are relatively weak and do not correlate with the level of background activity. (C) Dose–response curves for rapamycin and AP23102. Cells were exposed to the indicated concentrations of the dimerizer for 72 h and the percentage of recombined (X-gal-positive) cells was evaluated by direct counting. +FK corresponds to the level of excision observed when FK-506 is added with the dimerizer (200 nM against rapamycin and 500 nM against AP23109). The results shown correspond to the means of three experiments performed each time on three different 59.F2–60.F2 clones. (D) Kinetics of recombination in 59.F2–60.F2 cells (clone 14/1G8) following exposure to 10 nM AP23102. The dimerizer was added at t = 0 and removed at the indicated times. Genomic DNA was prepared either immediately after the removal of the dimerizer or at t = 72 h (lanes 3+, 6+, 12+, 18+ and 24+). Hybridization was performed with a probe homologous to an internal segment of the provirus (Fig. 2A.); NE corresponds to the fragment obtained when no recombination has occurred; E is the fragment obtained after recombination. (a) Kinetics of recombination when the dimerizer is present continuously for the indicated length of time. (b) Level of recombination observed at t = 72 h with the dimerizer present only for the indicated length of time, beginning at t = 0. (E) Cell proliferation following the transient activation of DiCre by AP23102. Cells were exposed to 10 nM of the dimerizer for 24 h. The cells were cultured for a further 2 (group +2d) or 6 (group +6d) days before the evaluation of proliferation over a subsequent 3-day period. Controls correspond to the cells not exposed to the dimerizer; AP23102 correspond to cells exposed to 10 nM AP23102 only during the period of evaluation of cell proliferation. The results shown are the means obtained with four different 59.F2–60.F2 clones.