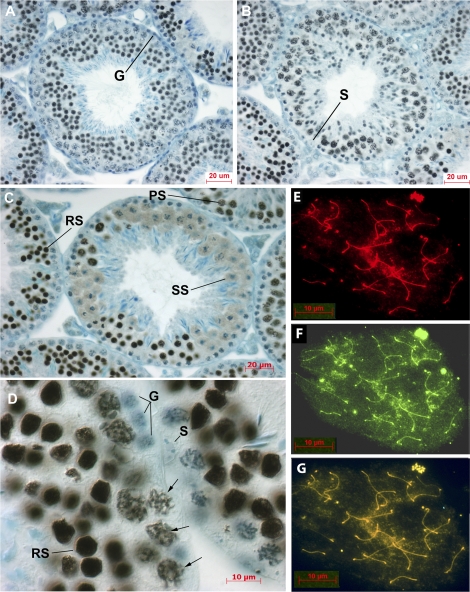
FIG. 1.
Localization of tNASP in mouse seminiferous tubules and on meiotic chromosomes. A and B) Sections through tubules at stage VI (A) and stage IX (B) show tNASP in leptotene, pachytene, and spermatid stages. Spermatogonia (G) and Sertoli cells (S) do not stain for tNASP. C) A stage XII tubule with diplotene and M-phase spermatocytes proceeding through meiosis to become secondary spermatocytes (SS). Round spermatids (RS) and pachytene spermatocytes (PS) can be seen staining for tNASP in adjacent tubules. D) Higher-magnification image of a seminiferous tubule shows tNASP localized in round spermatid nuclei (RS) and on chromatin in pachytene spermatocytes (arrows). Sertoli cell (S) and spermatogonia (G) nuclei are negative. Control staining with anti-NASP antibody absorbed with antigen was negative (data not shown). E–G) Surface-spread meiotic chromosomes demonstrate the localization of tNASP and HSPA2 in mouse primary spermatocytes. E) Staining for tNASP. F) Staining for HSPA2. G) Double staining for tNASP and HSPA2 on chromosomal spreads of mouse spermatogenic cells. Yellow/orange staining demonstrates the colocalization of tNASP and HSPA2. Bars = 20 μm (A–C) and 10 μm (D–G).