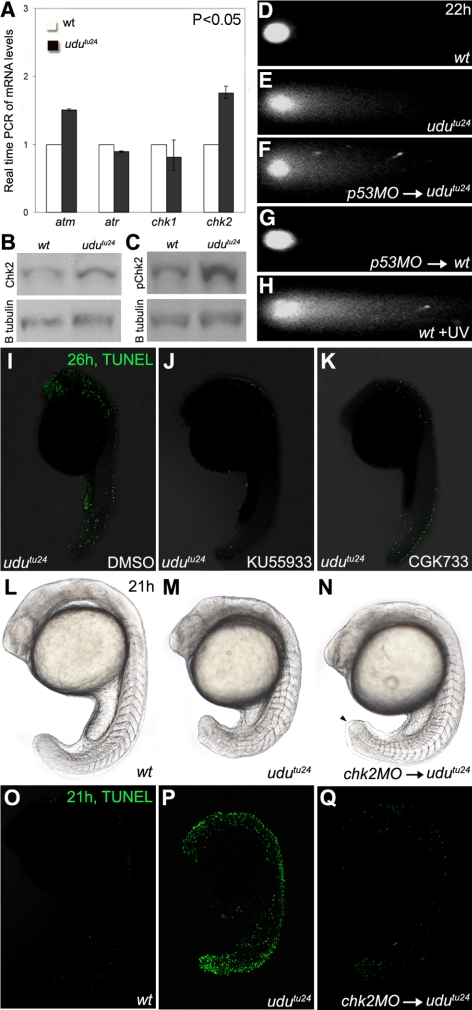
Figure 4.
Activation of Atm-Chk2 pathway in udutu24 mutants. (A) Real-time PCR of atm, atr, chk1 and chk2 mRNA levels extracted from 22 hpf embryos. The histogram is depicted as average ± SD format from three independent experiments (p < 0.05, Student's t test). The transcript level of atm and chk2 are significantly up-regulated in udutu24 mutants. (B and C) Western analyses showed increased levels of Chk2 and phospho-Chk2 (Ser33) in udutu24 embryos compared with wild-type embryos at 22 hpf. (D–H) Neutral single-cell electrophoresis or comet assay of untreated wild-type cells (D), untreated udutu24 cells (E), cells from p53-MO–injected udutu24 embryos (F), cells from p53-MO–injected wild-type embryos (G), and wild-type cells (H) isolated from embryos irradiated with UV for 1 h. The head is composed of intact DNA, whereas the tail consists of DNA with DSB. (I–K) TUNEL staining of udutu24 embryos treated with DMSO (I), 15 μM KU55933 (J), and 200 μM CGK733 (K) at 26 hpf. The number of TUNEL-positive cells is significantly reduced in embryos treated with KU55933 (62.5%; n =5/8) and CGK733 (80%; n = 8/10). (L–N) Phenotypes of chk2 morphants at 21 hpf. (N) Homozygous udutu24 embryos injected with chk2-MO have tail-tips that were not round-shaped but tapered (arrowhead). Somite structures are restored in 2.08 pmol chk2-MO–injected udutu24 embryos, compared with (M) noninjected udutu24 embryos. (O–Q) TUNEL staining of embryos at 21 hpf. (Q) The number of TUNEL-positive cells is significantly reduced in chk2-MO–injected udutu24 embryos, compared with (P) noninjected udutu24 embryos. (L and O) Wild-type embryos as the positive control for phenotypic observations and TUNEL assay, respectively.