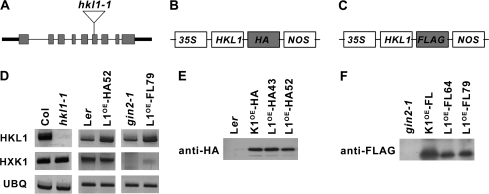
Fig. 1.
Molecular characterization of Arabidopsis HKL1 mutant and transgenic lines. (A) Schematic diagram showing the gene structure of HKL1 (At1g50460). Exons are indicated by grey rectangles, introns are indicated by the thinner lines. The location of the T-DNA insertion in hkl1-1 is shown with the open triangle. (B, C) Design of plasmid constructs used to transform Arabidopsis lines. HKL1-HA was used to transform Ler and HKL1-FLAG was used to transform gin2-1. Boxes are not drawn to scale. 35S, CaMV promoter; NOS, nopaline synthetase terminator; HA, 2 copies of the 10 amino acid haemagglutinin tag; FLAG, 1 copy of the 8 amino acid FLAG tag. (D) Transcript expression of HKL1 and HXK1 by semi-quantitative RT-PCR: Col and hkl1-1; Ler and HKL1-HA line 52; and gin2-1 and HKL1-FLAG line 79. AtUBQ5 mRNA was used as a control for the amount of template. PCR cycle numbers for HKL1, HXK1, and UBQ were 33, 30, and 30, respectively. L1OE, HKL1 overexpression. (E) Immunoblot analysis using anti-HA antibody and 1 μg protein from leaf extracts of Ler, HXK1-HA transgenic (K1OE-HA), and two HKL1-HA lines. (F) Immunoblot analysis using anti-FLAG antibody and 1 μg protein from leaf extracts of gin2-1, HXK1-FLAG transgenic (K1OE-FL), and two HKL1-FLAG lines.