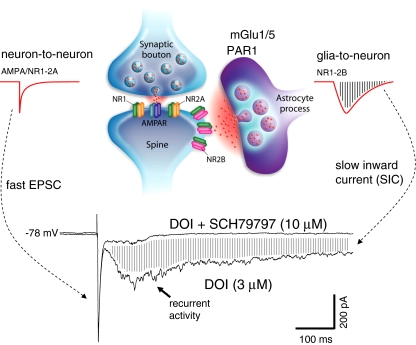
Fig. 4.
Proposed role of astrocytes in the generation of recurrent activity and slow inward currents (SICs). Drawing in upper panel depicts a synapse in which an adjacent astrocyte process slowly releases glutamate (in response to glutamate spillover) onto extrasynaptic NR2B receptors to give rise to glia-to-neuron SICs (adapted from Haydon and Carmignoto 2006). In contrast, the fast neuron-to-neuron response is of much shorter in duration. Traces below illustrate blockade of DOI-induced SICs by SCH79797, a selective antagonist of the astrocytic PAR1 receptor. Note the concomitant suppression of associated recurrent activity. Also note that the fast EPSC is unchanged as indicated by superimposition of the two traces (provided by G. Aghajanian)