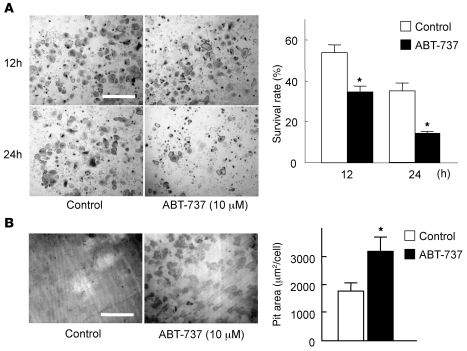
Figure 1. The Bcl-2/Bcl-xL inhibitor ABT-737 suppressed survival, but enhanced the bone-resorbing activity, of osteoclasts.
(A) For survival assay, we used bone marrow–derived osteoclasts generated on regular dishes in the presence of 100 ng/ml RANKL and 10 ng/ml M-CSF. On day 5 of culture (time 0), when osteoclasts were differentiated, they were further cultured with or without 10 μM ABT-737 and subjected to TRAP staining. The number of viable cells after 12 or 24 hours of ABT-737 treatment is shown as a percentage of morphologically intact osteoclasts compared with time 0. TRAP staining of representative cultures is also shown. (B) For pit formation assay, osteoclasts were generated by cocultures of osteoblasts and bone marrow cells on collagen gel–coated dishes in the presence of 10 nM 1α,25(OH)2vitamin D3 and 1 μM PGE2. On day 6 of culture, when osteoclasts were differentiated, cells were dispersed by treating with 0.1% collagenase for 10 minutes, resuspended in α-MEM containing 10% FBS, and replated on dentine slices in the presence or absence of 10 μM ABT-737. After 24 hours of culture, cells were removed by treating the dentine slices with 1M NH4OH, and pit area was visualized by toluidine blue staining and quantified by image analysis system. Resorption pits of representative cultures are also shown. (A and B) Results are mean ± SD of 6 cultures. *P < 0.01 versus untreated control. Scale bars: 500 μm.