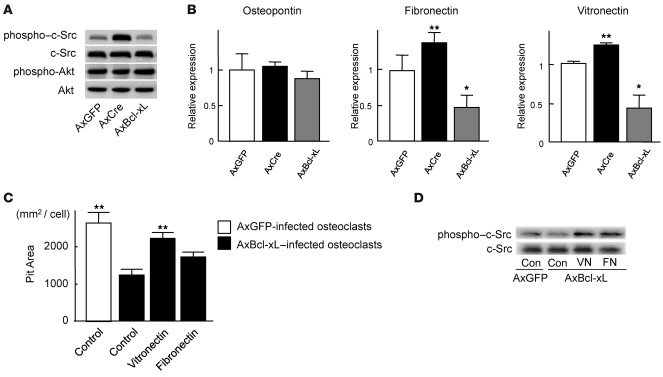
Figure 7. Bcl-xL reduced c-Src activity in osteoclasts by suppressing the expression of ECM proteins.
(A) Western blotting with anti–phospho–c-Src antibody and anti–phospho-Akt antibody. Osteoclasts generated from Bcl-xfl/fl mouse bone marrow cells were infected with AxGFP, AxCre, or AxBcl-xL. After 24 h of infection, the lysates were subjected to Western blotting. c-Src was activated in Bcl-x cKO osteoclasts, while no difference in Akt activation was observed. The amount of total c-Src or Akt did not appear to differ. (B) mRNA expression of osteopontin, vitronectin, and fibronectin by real-time RT-PCR. Vitronectin and fibronectin expression increased in Bcl-x cKO osteoclasts and decreased in Bcl-xL–overexpressing osteoclasts. Results are mean ± SD of 6 samples. *P < 0.01, **P < 0.05 versus AxGFP-infected cells. (C) Effect of ECM protein coating on bone-resorbing activity of AxBcl-xL–infected osteoclasts. When AxBcl-xL–infected osteoclasts were cultured on vitronectin- or fibronectin-coated dentine slices, the negative effect of Bcl-xL overexpression on bone resorption was partially reversed, and vitronectin-coated dentine slices showed a significant increase in pit area. Results are mean ± SD of 4 cultures. **P < 0.05 versus AxBcl-xL–infected osteoclasts cultured on uncoated control dentine slices. (D) Western blotting with anti–phospho–c-Src antibody and anti-Src antibody. c-Src activity suppressed by AxBcl-xL expression in osteoclasts was partially restored by plating the cells onto vitronectin- or fibronectin-coated dishes. The total amount of c-Src did not appear to differ.