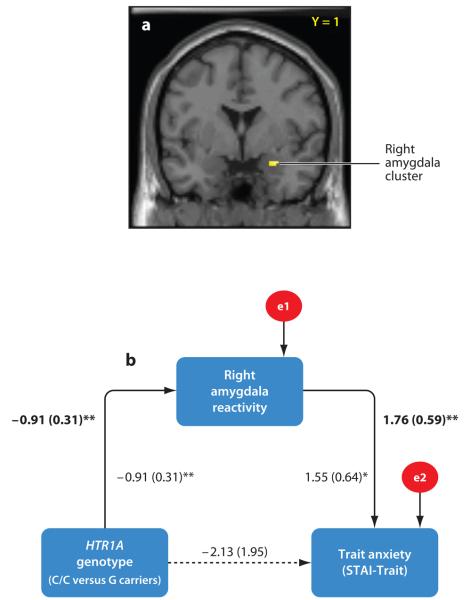
Figure 2.
The HTR1A genotype indirectly predicts trait anxiety through amygdala reactivity (adapted from Fakra et al. 2009). (a) Statistical parametric map illustrating the right amygdala cluster correlated with both HTR1A genotype and trait anxiety. Single-subject activation values from the maximal voxel in this cluster were entered into path analyses. (b) Path model testing indirect effects of the HTR1A genotype on trait anxiety. Lines are labeled with nonstandardized path coefficients and standard errors in parentheses. Coefficients in bold above the line represent values from the trimmed model, whereas coefficients in Roman represent values from the full model with all paths included. Indirect effects of the HTR1A genotype on trait anxiety were significant (αβ = −1.60, SE = 0.73, P < 0.05), whereas direct effects were nonsignificant and dropped from the model. e1 and e2 represent the residual variances not explained by model variables. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.