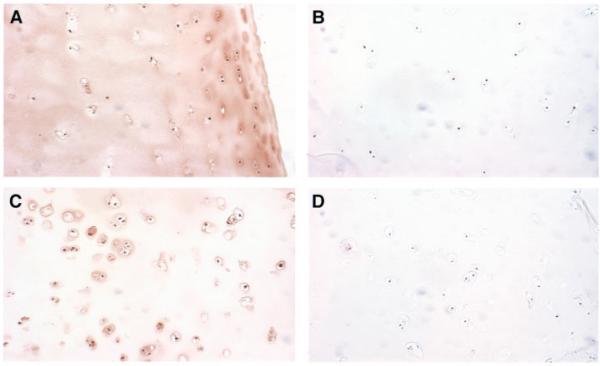
Figure 2.
Immunolocalization of extracellular superoxide dismutase (EC-SOD) in normal and osteoarthritic (OA) human cartilage. Immunohistochemistry of EC-SOD in human cartilage samples was performed using polyclonal antibody to human EC-SOD and peroxidase staining. Negative controls were prepared with EC-SOD-absorbed antiserum. A, Cartilage section from a 37-year-old male cadaver donor, showing significant EC-SOD staining in the matrix surrounding the chondrocytes, with variable light staining intracellularly. B, Negative control for the section shown in A. C, Cartilage from a 58-year-old woman with OA, showing increased cellularity, degeneration of the superficial cartilage layer, and pronounced lack of matrix staining. Note the increased intracellular staining for EC-SOD compared with the nonarthritic chondrocytes. D, Negative control for the section shown in C. (Original magnification × 100.)