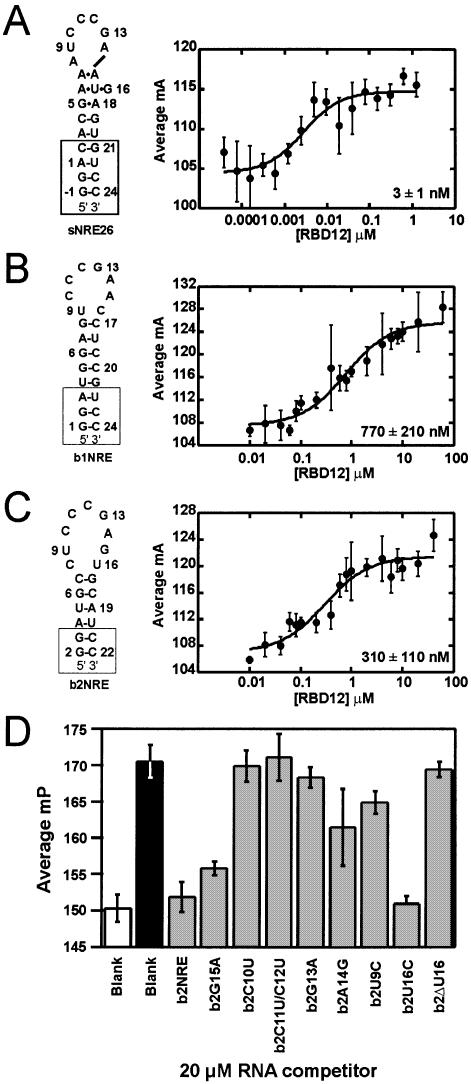
Figure 1.
Secondary structure representations (left) and nucleolin RBD12 binding isotherms (right) for (A) sNRE26, (B) b1NRE (nucleotides U3–G21 correspond to mouse 5′ ETS: 515–532) and (C) b2NRE (nucleotides A4–U20 correspond to mouse 5′ ETS: 562–578) (EMBL database accession No. M20154) (11). Nucleotides added for the purpose of transcription and stem stability are shown in boxes. The numbering of sNRE26 and b2NRE has been adjusted to correspond to the original sNRE construct (18). Binding isotherms were generated with 2 nM 5′-fluorescein-labeled NRE and varying nucleolin RBD12 concentrations. Each point is the average of five measurements, and error bars represent the standard deviation of those measurements. Data were fit to equation 2, and all R2 values are >95%. (D) Competition experiments of nucleolin RBD12 binding to b2NRE. Millipolarization (mP) values of free 5′-fluorescein-labeled b2NRE (Flb2) (white), Flb2 in the presence of 10 µM nucleolin RBD12 (black), and Flb2 in the presence of 10 µM nucleolin RBD12 and 20 µM (10 000× probe concentration) specified competitor RNA (gray).