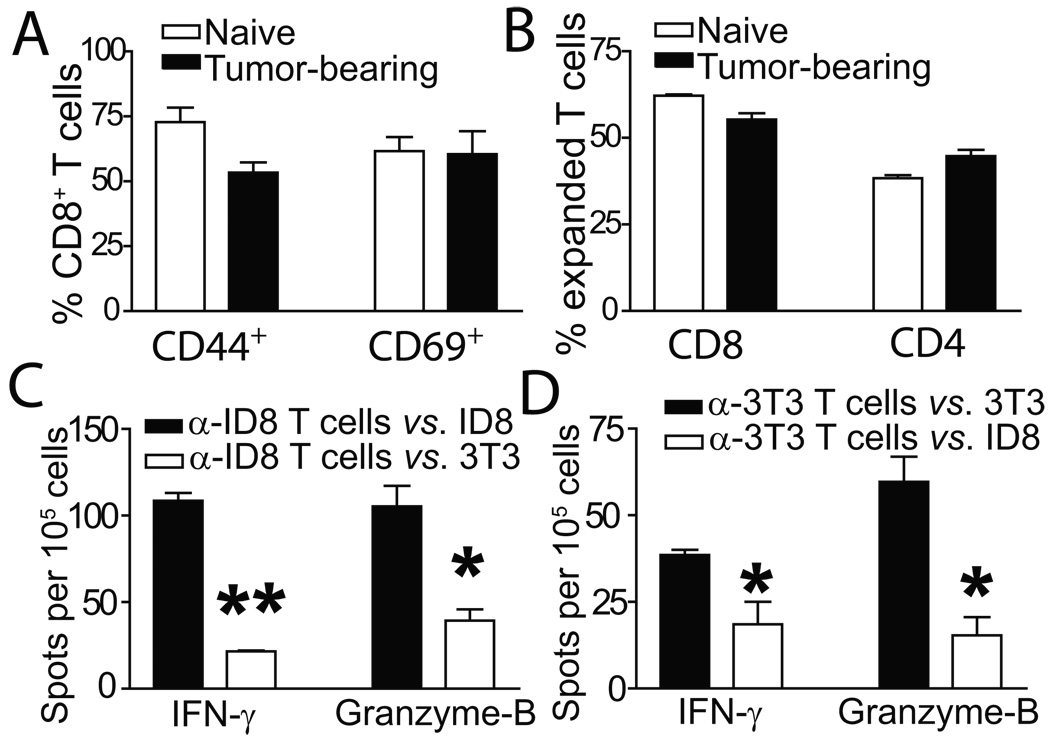
Figure 1. Phenotypic characterization of tumor-reactive and irrelevantly primed T cells.
(A) Activation status of T cells from either healthy (naive) or ID8-Defb29/Vegf-a tumor-bearing (tumor-bearing) mice primed to ID8-Defb29/Vegf-a antigens. Representative of 3 independent experiments. (B) T cells expanded from tumor-bearing or healthy mice show comparable proportions of CD8 vs. CD4 T cells. (C) IFN-γ and granzyme-B ELISPOT analyses of naïve T cells primed to ID8-Defb29/Vegf-a antigens, in response to their cognate tumor antigen (α-ID8 T cells vs. ID8), or NIH-3T3 fibroblasts (α-ID8 T cells vs. 3T3). Representative of 2 independent experiments (n=6/group, total). (D) Similar ELISPOT analysis performed with naïve T cells primed to irrelevant NIH-3T3 fibroblasts (*- P<0.05; **- P<0.01).