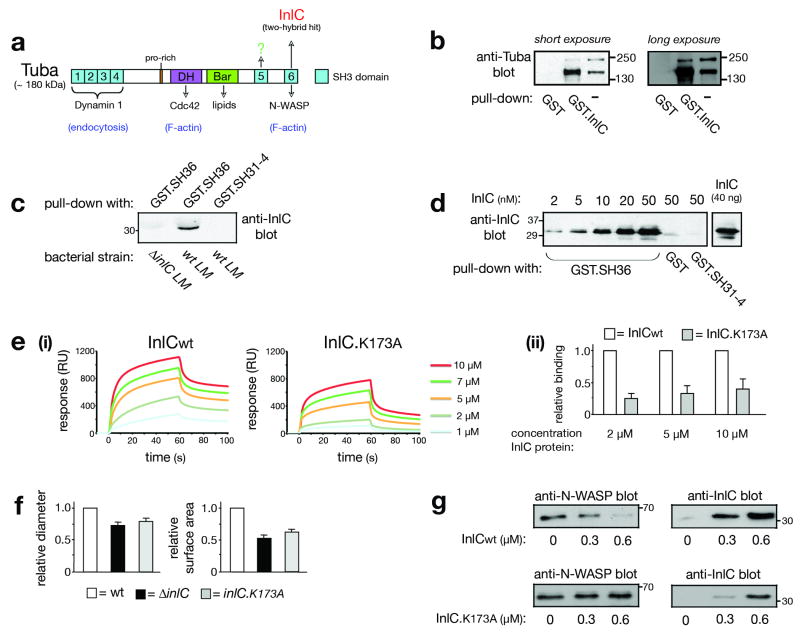
Figure 2. InlC interacts with the mammalian adaptor protein Tuba.
(a) Structure of Tuba. SH3, Dbl homology (DH), and Bin-Amphiphysin-Rvs (Bar) domains are indicated. The last SH3 domain (SH36) interacts with InlC or human N-WASP19. Other ligands of the first four SH3 (SH31-4), DH, or Bars domain are indicated. In addition to full-length Tuba (∼180 kDa), isoforms lacking SH31-4, but retaining the DH, Bar, SH35, and SH36 domains, exist19,20. (b) InlC associates with ∼ 180 and ∼150 kDa Tuba isoforms from Caco-2 BBE1 cells. A GST-InlC fusion protein was incubated with cell lysates and precipitated. Precipitates were immunoblotted with antibodies against the Tuba SH36 domain. (c) The Tuba SH36 domain associates with secreted InlC. Caco-2 BBE1 cells were infected with wild-type (wt) or ΔinlC strains of L. monocytogenes (LM) for 7 h. Cell lysates were used for precipitation with GST proteins containing SH36, or the SH31-4 region as a control. (d) InlC interacts directly with SH36. GST proteins containing SH36, SH31-4, or GST alone (10 nM) were incubated with the indicated concentrations of InlC and precipitated. InlC was detected by immunoblotting. The last lane is a loading control. (e) An RxxK sequence in InlC participates in binding to SH36 (i). Binding of wild-type InlC protein (InlCwt) or InlC.K173A, as measured by SPR. Representative data from a single experiment is shown. Data from 3-4 experiments were used to estimate equilibrium dissociation constants (KD) of 9.0 ± 3.5 and 58 ± 12.3 μM for wild-type InlC and InlC.K173A, respectively. P = 0.0007. (ii). Relative binding of wild-type (wt) InlC and InlC.K173A to SH36. The data is average ± s.e.m. (n=3). (f) An RxxK sequence in InlC is needed for efficient spreading. Average relative plaque diameters (i) or surface areas (ii) ± s.d. (n=3) of wild-type (wt), ΔinlC, or inlC.K173A strains of Listeria are presented. (g) InlC displaces N-WASP from SH3-6. 10 nM GST-SH36 was incubated with 10 nM of N-WASP in the presence of the indicated concentrations of wild-type InlC (InlCwt) or InlC.K173A for 2.5 h. GST-SH36 was precipitated, and N-WASP (left panels) or InlC (right panels) detected by immunoblotting.