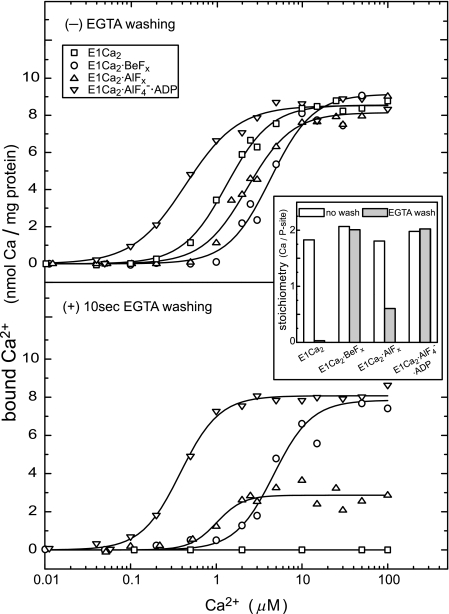
FIGURE 4.
Ca2+ binding and occlusion at transport sites. The E1Ca2 state ATPase of SR vesicles in various concentrations of 45Ca2+ and 15 mm MgCl2 was incubated with BeFx, AlFx, and AlFx·ADP or without these compounds (E1Ca2) for 30 min at 25 °C. The amounts of bound (upper panel) and occluded (lower panel) 45Ca2+ were determined without and with the perfusion of the membrane filter with a 5 mm EGTA-containing washing solution (without CaCl2 and fluoride compounds otherwise as the above incubation solution). The nonspecific Ca2+ binding was determined by including 10 μm thapsigargin before the addition of fluoride compounds, and subtracted. When ADP was used for E1Ca2·AlF4−·ADP, 5 μm A23187 was included to avoid Ca2+ accumulation in the vesicles by ATP produced from ADP due to adenylate kinase in the vesicles. In the inset, the stoichiometries of bound Ca2+ (open bars) and occluded Ca2+ (closed bars) to the phosphorylation site (P-site) were determined at saturating 50 μm 45Ca2+. Solid lines in the upper panel show the least squares fit to the Hill equation. K0.5 of Ca2+ and Hill coefficients obtained were 1.3 μm and 1.7 (E1Ca2), 4.3 μm and 1.7 (E1Ca2·BeFx), 2.3 μm and 1.7 (E1Ca2·AlFx), and 0.4 μm and 1.4 (E1Ca2·AlF4−·ADP). In the lower panel, the values for E1Ca2·BeFx and E1Ca2·AlF4−·ADP are essentially not altered by EGTA washing (4.7 μm and 1.9, and 0.4 μm and 1.9, respectively).