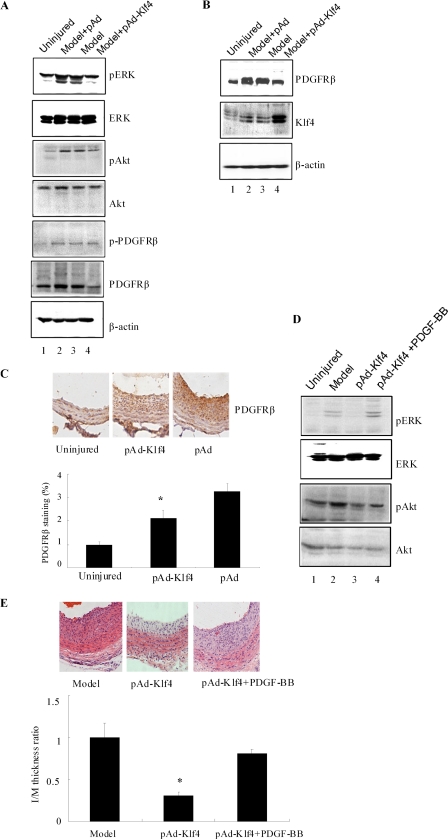
FIGURE 7.
Inhibition of PDGFβ receptor expression and signaling contributes to Klf4-mediated reduction in injury-induced neointimal hyperplasia. A and B, 3 (A) and 14 (B) days after pAd- and pAd-Klf4-infected animals were subjected to vascular injury, the injured arteries were harvested and analyzed by Western blotting using the indicated antibodies. Note the decreased expression of PDGFβ receptor in pAd-Klf4-infected rats following injury. The blots are representative of three independent animals. C, 14 days after vascular injury, the arterial sections were subjected to immunohistochemical staining using anti-PDGFR. PDGFR staining was evaluated as indicated in Fig. 1C. *, p < 0.05 versus control pAd group. D and E, PDGF-BB was given locally to pAd- and pAd-Klf4-infected animals that were subjected to vascular injury. D, 3 days later, the injured arteries were harvested and analyzed by Western blotting using the indicated antibodies. The blots are representative of three independent animals. E, 14 days later, the arterial sections were subjected to histological analysis. Neointimal formation was evaluated by calculating the I/M ratio as indicated in Fig. 1A. *, p < 0.05 versus model group (n = 6 in each group).