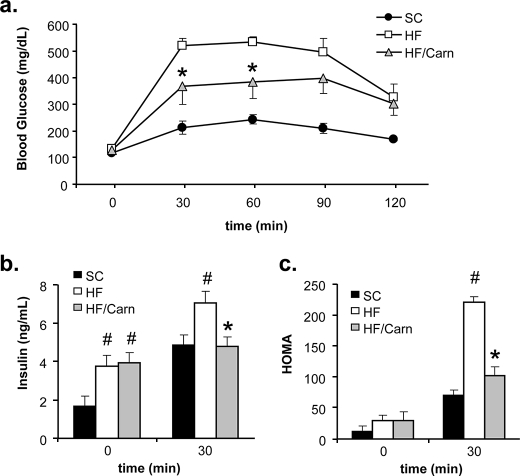
FIGURE 3.
Carnitine supplementation improved whole body glucose tolerance. Male Wistar rats were fed either a standard chow (SC) or high fat (HF) diet for 12 months, with or without oral carnitine therapy during the final 2 months (HF/Carn). Intraperitoneal glucose tolerance tests (a) were performed 5 weeks after initiation of carnitine therapy. Plasma insulin values obtained at basal and 30 min post glucose injection (b) were used to calculate the homeostatic assessment model index of insulin resistance (c). Data represent means ± S.E. from 5–8 animals per group. Results were analyzed by Student's t test for between group differences, and a paired t test was applied to detect the within group effect of carnitine. #, p < 0.05 difference versus SC controls; *, p < 0.05 due to carnitine supplementation.