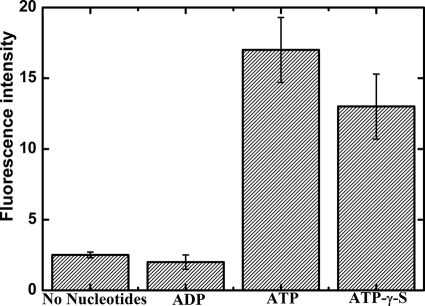
FIGURE 5.
Nucleotide binding but not hydrolysis is required for casein translocation by PAN and degradation by the associated 20 S proteasome. The ability of ADP, ATP, and ATPγS to induce gate opening in the ATPase (PAN) and to promote translocation into the 20 S proteasome was estimated by monitoring the effect of these nucleotides on β-casein degradation. β-Casein was subjected to degradation by the archaeal PAN-20 S complex in the presence of ADP, ATP, ATPγS, or in the absence of nucleotides. The magnitude of β-casein degradation was estimated by the fluorescamine assay (43).