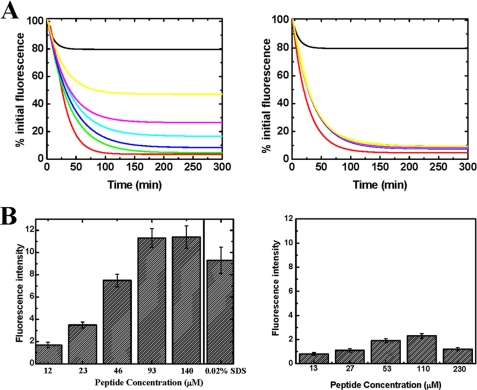
FIGURE 6.
The C-terminal peptide of PAN inhibits degradation of YFP-ssrA. A, left panel, the loss of YFP-ssrA fluorescence was measured as a function of time in the presence of the PAN C-terminal peptide. The green, blue, cyan, purple, and yellow curves represent reaction mixtures with increasing amounts of the peptide (20, 40, 60, 80, and 160 μm, respectively). Right panel, similar reactions as in A were carried out in the presence of the same concentrations of a nonspecific peptide. B, the C-terminal region of PAN induces gate opening in the α-ring of the 20 S proteasome. Left panel, β-casein degradation by the latent 20 S proteasome in the presence of increasing amounts of the PAN C-terminal peptide and in the presence of 0.02% SDS as a control to chemically induce gate opening. Right panel, β-casein degradation by the latent 20 S proteasome in the presence of increasing amounts of a mixture of nonspecific peptides. The degradation of β-casein was estimated by the fluorescamine assay. The contribution of the peptides themselves was determined in separate reaction and subtracted from the β-casein degradation reactions presented.