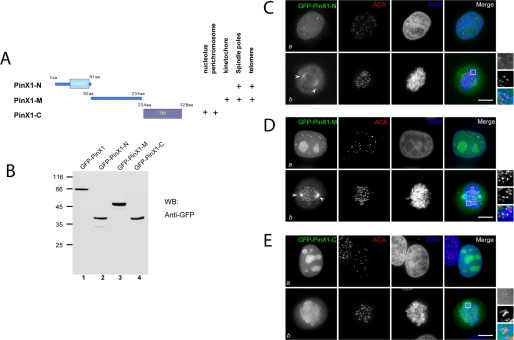
FIGURE 2.
Characterization of PinX1 structure-localization relationship. A, schematic illustration of PinX1 functional domains and summary of PinX1 structure-localization relationship. aa, amino acids. B, validation of exogenous expression of GFP-PinX1 and its deletion mutants. WB, Western blot; GFP, green fluorescent protein. C, this montage represents optical images collected from PinX1-N transfected HeLa cells triply stained for GFP-PinX1-N (green), ACA (red), and DAPI (blue). In interphase (panel a), it is readily apparent that GFP-PinX1-N appears as six tiny spots in the nucleus. No co-distribution of PinX1 with ACA is observed. In prometaphase (panel b), GFP-PinX1-N labeling appears at the spindle poles (arrowheads). Bar, 10 μm. D, this montage represents optical images collected from PinX1-M transfected HeLa cells triply stained for GFP-PinX1-M (green), ACA (red), and DAPI (blue). In interphase (panel a), it is readily apparent that PinX1 is concentrated in the nucleus, appearing as 7–8 bright spots. No co-distribution of PinX1 with ACA was observed. In prometaphase (panel b), GFP-PinX1-M labeling appears at the spindle poles (arrows) in addition to kinetochore localization. Bar, 10 μm. E, this montage represents optical images collected from PinX1-C-transfected HeLa cells triply stained for GFP-PinX1-C (green), ACA (red), and DAPI (blue). In interphase (panel a), it is readily apparent that PinX1-C is concentrated in the nucleolus, appearing as 5–6 bright spots. In general, PinX1-C and ACA are not co-localized (panel a). In prometaphase (panel b), GFP-PinX1-C labeling appears at perichromosomal regions. Bar, 10 μm.