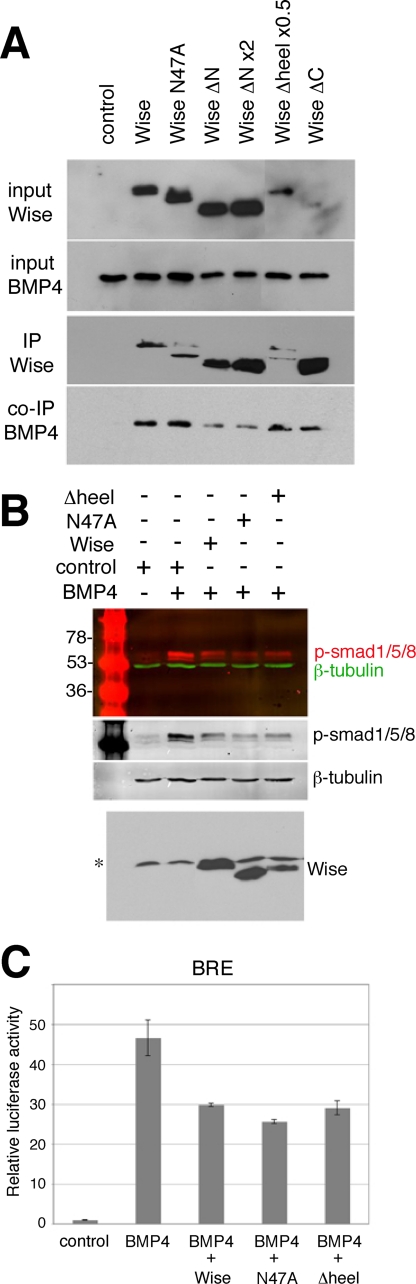
FIGURE 5.
Effect of Wise deletion constructs on BMP4. A, immunoprecipitation (IP) assay. HEK293 cells were transfected with control or FLAG-tagged Wise constructs, as indicated above, together with a construct encoding Myc-tagged BMP4. The amounts of DNA used for Wise(ΔN) and Wise(Δheel) were adjusted in a manner similar to that in Fig. 4A. The conditioned media were collected from each and used for immunoprecipitation with anti-FLAG antibody. Input samples are shown in the top two panels. Immunoprecipitation of Wise and BMP4 is shown in the bottom two panels. There was no significant difference in the precipitation efficiency except that Wise(ΔN) showed less precipitation of BMP4 relative to the abundant amount of Wise(ΔN) inputs. This trend was not consistently seen in other experiments. B, phospho-Smad1/5/8 assay. HEK293 cells were treated with a mixture of recombinant BMP4 protein and Wise conditioned medium (Wise, N47A, or Δheel), as indicated, and the cells were collected to detect phosphorylated Smad (p-Smad)1/5/8 (red) on a Western blot with a fluorescent secondary antibody. β-Tubulin (green) is a loading control. Each channel is also shown in black and white. The bottom panel shows a Western blot of input Wise media. *, a nonspecific band. C, BRE reporter assay. HEK293 cells were transfected with BMP4 and Wise constructs, as indicated, together with BRE and control Renilla reporters. The graph shows the relative luciferase units, normalized to the control sample (no BMP4). Wise, N47A, and Δheel suppress BMP4 activity.