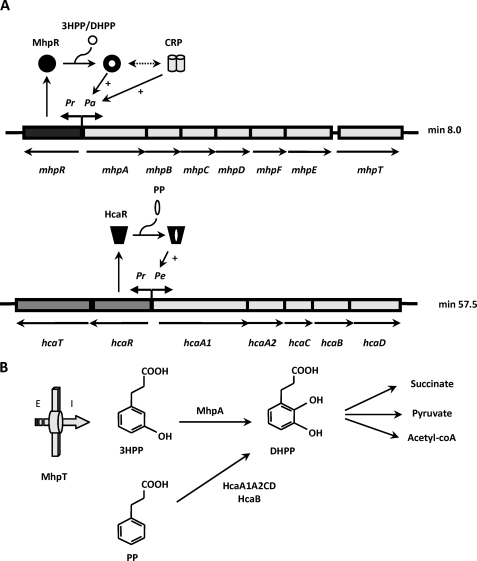
FIGURE 1.
Regulation and biochemistry of the mhp and hca clusters encoding the pathways for the catabolism of 3HPP and PP, respectively, in E. coli. A, the organization of the catabolic (mhpABCDFE and hcaA1A2CBD), transport (mhpT and hcaT), and regulatory (mhpR and hcaR) genes as well as their regulation by MhpR and HcaR and the global regulator CRP are represented. The thick arrows indicate the direction of gene transcription. Pr, Pa, and Pe are promoter regions. The black circle and the black trapezoid mean the inactive forms of the MhpR activator and the HcaR activator, respectively; the white circle represents the inducer, and + indicates transcriptional activation. The double-headed arrow means synergistic transcription activation by MhpR and CRP. B, scheme of the biochemistry of 3HPP and PP catabolic pathways. The 3HPP transport protein (MhpT) is represented by a thick arrow. E and I indicate outside and inside the cell, respectively. A brief scheme of the pathways including the final products and the first step for the transformation of 3HPP and PP into the common intermediate DHPP by the action of the MhpA monooxygenase and the HcaA1A2CD/HcaB dioxygenase/dihydrodiol-dehydrogenase, respectively, is shown.