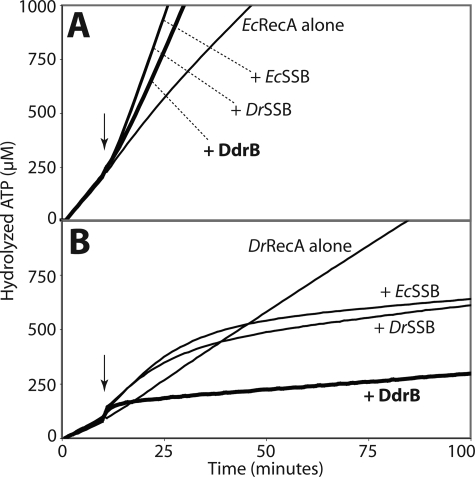
FIGURE 8.
Similarly to the SSB proteins, DdrB enhances EcRecA and inhibits DrRecA ssDNA binding activities. RecA ssDNA-dependent ATPase activity, proportional to the amount of RecA bound to DNA, was monitored at 380nm to follow the loss of NADH used in the coupled ATP regeneration system. The reactions were carried out at 37 °C. 3 μm RecA protein was added first to M13mp18 circular ssDNA (5 μm nucleotides), and the reactions were initiated by the addition of 3 mm ATP. The SSB or DdrB proteins (0.5 μm each) were added 10 min after (arrow). Curves from typical experiments are represented. A, effects on E. coli RecA. The kcat of EcRecA on ssDNA alone is 11.42 ± 0.98 min−1. Addition of EcSSB and DrSSB enhanced EcRecA ATPase activity to kcat values of 30.76 ± 0.48 min−1 and 30.26 ± 1.10 min−1, respectively. Addition of DdrB had a similar but lesser effect on EcRecA yielding a kcat of 24.80 ± 0.47 min−1 (thick line). B, effects on D. radiodurans RecA. The kcat value for DrRecA alone is 6.89 ± 0.15 min−1. Addition of EcSSB or DrSSB produced an initial enhancement to kcat values of, respectively, 10.72 ± 0.36 min−1 and 9.45 ± 0.59 min−1 followed by a slow inhibition to kcat values of 0.77 ± 0.52 min−1 and 1.13 ± 0.84 min−1 with EcSSB and DrSSB, respectively. Addition of DdrB immediately decreased DrRecA ATPase activity to a kcat value of 0.59 ± 0.09 min−1 (thick line).