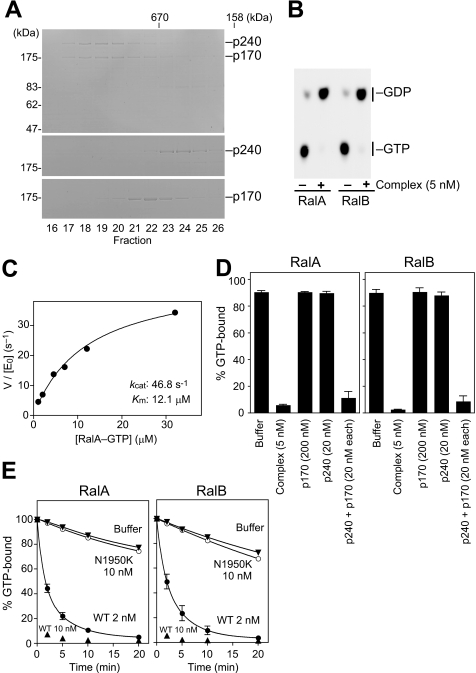
FIGURE 2.
Biochemical and catalytic properties of the recombinant p240-p170 complex. A, chromatographic comparison of the recombinant p240-p170 complex (top), p240 alone (middle), and p170 alone (bottom) on Superose 6 gel filtration chromatography. Gels were Coomassie Blue-stained. B, autoradiograph showing that the recombinant complex stimulates Ral GTPase activity. [α-32P]GTP-loaded RalA or RalB were incubated at 30 °C for 10 min with (+) or without (−) the recombinant complex (5 nm). C, kinetic analysis of the recombinant p240-p170 complex. Initial rates of GTP hydrolysis on RalA were determined at 30 °C at increasing concentrations of GTP-bound RalA by the filter binding assay. The recombinant p240-p170 complex was used at 1 nm ([E0]). GTPase reaction rates were fitted to the Michaelis-Menten equation to give Km (12.1 μm) and kcat (46.8 s−1) values of the reaction. D, p240 requires p170 for GAP activity. [γ-32P]GTP-loaded RalA or RalB were incubated at 30 °C for 10 min with the recombinant complex, p240 alone, p170 alone, or a mixture of separately purified p240 and p170 at the indicated concentrations (mean ± S.E., n = 3). E, the N1950K mutation abrogates p240 GAP activity. [γ-32P]GTP-loaded RalA or RalB were incubated at 30 °C for the indicated periods with the wild-type complex (WT; 2 nm or 10 nm) or the mutant complex (N1950K; 10 nm) (mean ± S.E., n = 3).