Figure 3. IFN-β is required in vitro during cDC-T cell contact as well as in vivo during cDCs development.
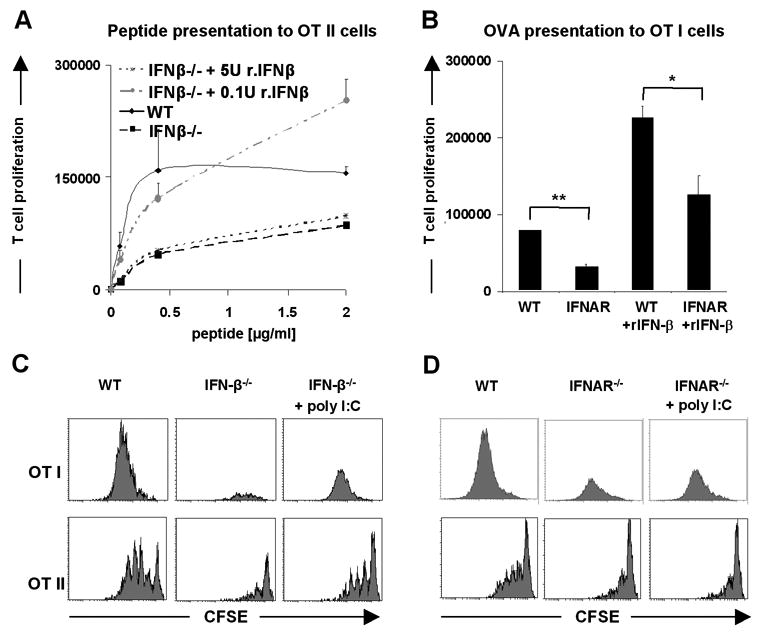
(A) Addition of low amounts of murine recombinant IFN-β (0.1 U/ml) leads to efficient recovery of impaired ability to present antigen by splenic cDCs from IFN-β-/- mice. OT I and OT II cells after purification were labeled with CFDA(SE). Splenic cDCs from WT and IFN-β-/- mice were sorted out from spleens of at least three mice, loaded with indicated concentration of OVA peptide for 1h, washed intensively and cocultured with T cells for 2.5 days in presence of recombinant murine IFN-β. (B) Enhanced proliferation of T cells accompanying impaired function of IFNAR-/- cDCs in the presence of exogenously added low amounts of rIFN-β. Splenic cDCs from WT and IFNAR-/- mice were sorted out from spleens of at least three mice per group, loaded with 250 μg/ml of OVA protein for 1h, washed intensively and cocultured with OT I T cells for 2.5 days in presence of 0.1 U/ml of recombinant murine IFN-β. (C and D) In vivo induction of IFNs by poly I:C leads to partial restoration of function of splenic cDCs from IFN-β-/- mice. WT, IFN-β-/- and IFNAR-/- mice were treated with poly I:C together with OVA or OVA alone, 24h later splenic cDCs were sorted out and incubated in vitro with CFDA(SE) labeled OT I or OT II cells for 2.5 days. The proliferative response of T cells was enumerated by flow cytometry. Data are representative of two independent experiments.
