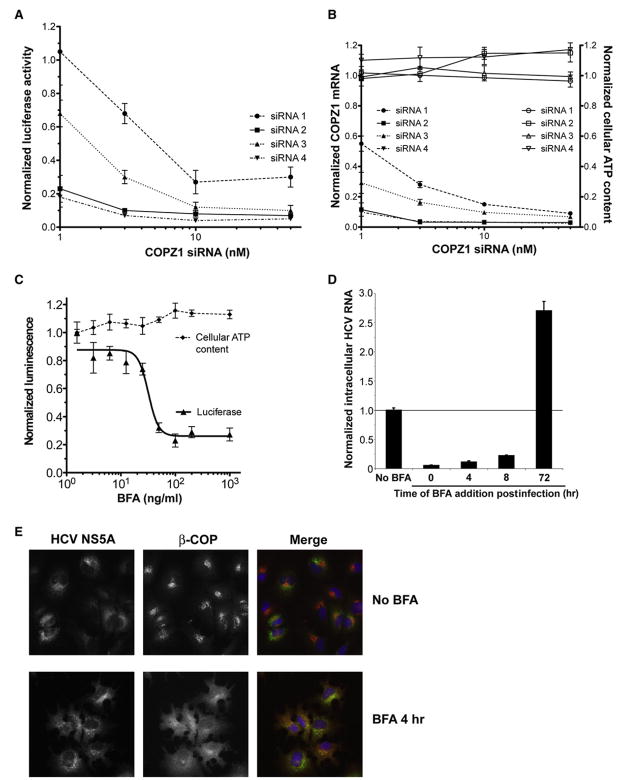
Figure 3. The COPI Complex Supports HCV Replication Early in the Viral Lifecycle.
(A) Individual siRNA duplexes against COPZ1 block replication of the full-length HCV replicon OR6 in a concentration-dependent manner. OR6 cells were transfected with the indicated siRNA duplexes for 64 hr and then assayed for luciferase activity. Values were obtained from quadruplicate wells in two independent experiments and are mean ± SD.
(B) Individual siRNA duplexes against COPZ1 deplete COPZ1 transcripts in a dose-dependent manner without detectable cytotoxicity. OR6 cells transfected with the indicated siRNA duplexes as in (A) were assayed for cellular ATP content (open symbols) or for COPZ1 transcript levels by quantitative real-time PCR (closed symbols). Values were obtained from triplicate qPCR measurements from duplicate wells in two independent experiments and are mean ± SD.
(C) Brefeldin A (BFA), a pharmacologic inhibitor of COPI function, blocks replication of the OR6 full-length replicon. OR6 cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of BFA for 24 hr and then assayed for luciferase activity (triangles) or cellular ATP content (diamonds). Values were obtained in quadruplicate and are mean ± SD.
(D) BFA blocks replication of the infectious JFH1 isolate early in viral infection and blocks HCV secretion late in infection. BFA was added at 100 ng/mL to Huh7.5.1 cells at the indicated times relative to the time of JFH1 infection. Intracellular HCV RNA was quantified by qPCR at 20 hr of BFA treatment and normalized to HCV RNA from mock treated cells. Values were obtained from triplicate qPCR replicates from duplicate wells and are mean ± SD.
(E) Preformed NS5A-positive structures are resistant to BFA treatment. OR6 cells were treated with 100 μg/mL BFA (lower panels) or 1% ethanol (upper panels) for 4 hr and then processed for immunofluorescence for HCV NS5A (left panels) and HCV NS5A (middle panels). Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue). BFA causes dissociation of β-COP from the Golgi apparatus within minutes of treatment.