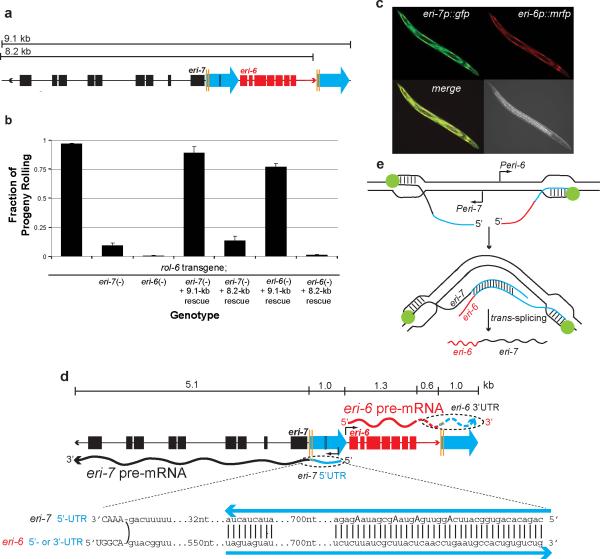
Figure 2. The eri-6/7 mRNA is formed by local trans-splicing.
a, Schematic of eri-6/7 locus used for rescue: 9.1-kb fragment; and 8.2-kb fragment missing the second repeat. b, Rescue of eri-6/7(mg411)-induced silencing of the mgIs30 transgene-conferred rolling phenotype. Number of broods scored = 28, 28, 18, 19, 38, 29 and 18, respectively. Multiple transgenic lines assayed. Error bars: s.e.m. c, The eri-6 and eri-7 promoters express in overlapping tissues (hypodermis and head neurons). eri-6 and eri-7 promoters were fused to rfp and gfp, respectively. d, 5′-RACE experiments show that eri-6 and eri-7 are expressed as separate pre-mRNAs with sufficient nucleotide homology to base-pair, thus facilitating trans-splicing. eri-7 pre-mRNA starts 775 nucleotides (nt) upstream of exon 1, whereas eri-6 pre-mRNA starts 100 nt upstream of eri-6 exon 1 (black arrows). Edited nucleotides (A to G indicative of A to I) in eri-7 pre-mRNA are in bold capital letters. Blue arrows: direct repeats. Capital letters: exon sequence. Curved line: trans-splicing juncture. e, Model of eri-6/7 trans-splicing. eri-6 and eri-7 pre-mRNAs are locally co-transcribed in the same cells. The pre-mRNAs may form a dsRNA intermediate that facilitates co-transcriptional trans-splicing.