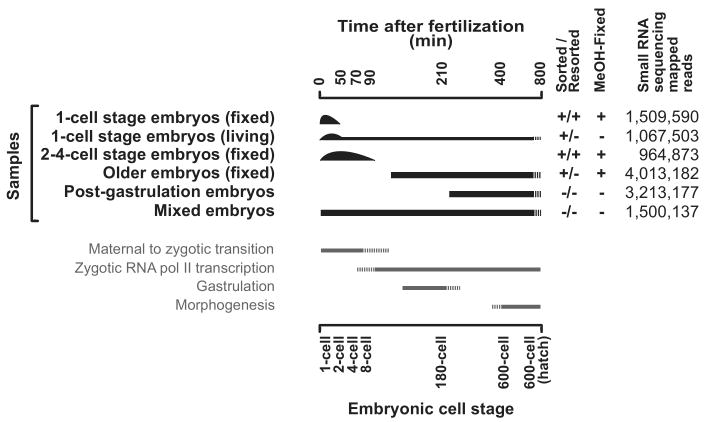
Figure 2.
Dissecting small RNA expression during embryogenesis.
Summary of the six samples used for small RNA cloning and next-generation sequencing (Illumina). Two different one-cell stage samples were obtained by embryo Fluorescent Activated Cell Sorting (eFACS): (i) The living-sorted one-cell stage embryo sample represents a mixed embryo sample enriched in one-cell stage embryos. (ii) The vast majority of the fixed and twice-sorted (resorted) one-cell stage embryo sample consists of one-cell embryos (>98%) in which embryos are mainly in very early phases of their first cell cycle (Fig. 1). The two-to-four-cell stage sample was obtained by resorting fixed embryos and represents a mixture of one-cell to eight-cell embryos strongly enriched in two-to-four-cell stage embryos (Supplementary Fig. 1). Two older embryo populations were generated by (i) eFACS of GFP negative embryos, which represent a mixed embryo population depleted in early embryos and by (ii) harvesting post gastrulation embryos by allowing isolated embryos to develop for 3 hours at 20°C. Finally, also a mixed embryo population was obtained. The total number of successfully mapped small RNAs in each sample is tabulated to the right.