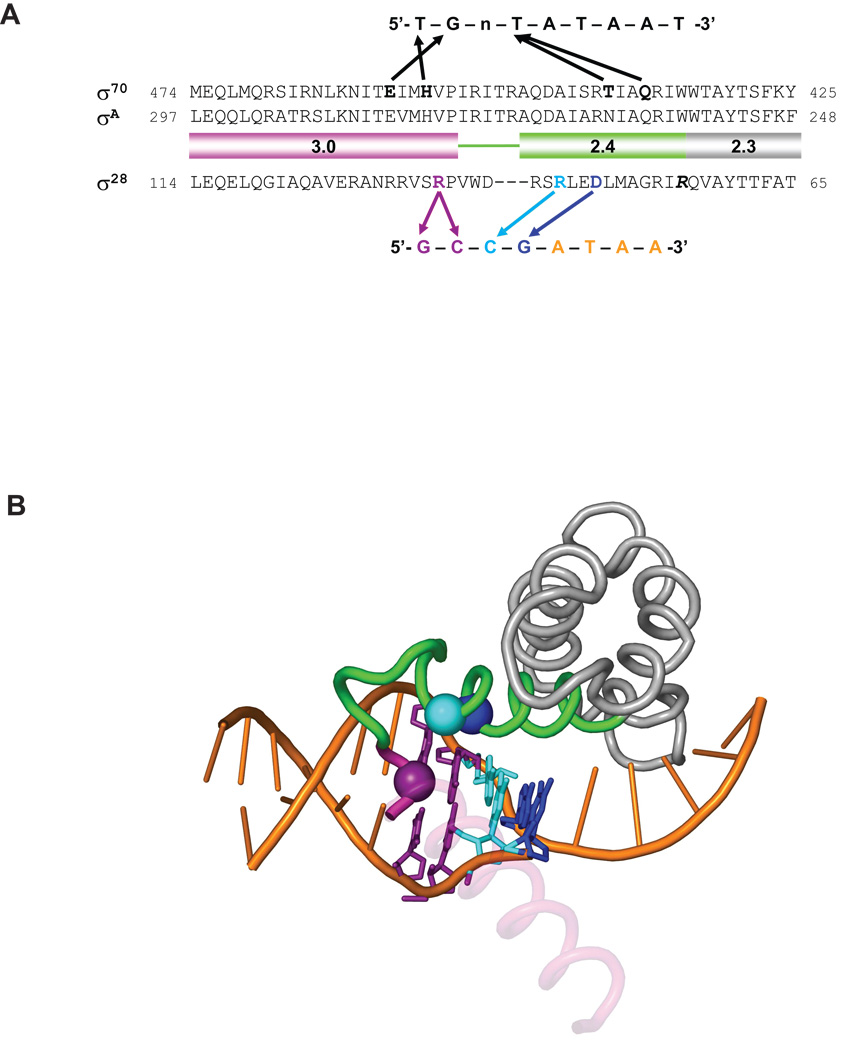
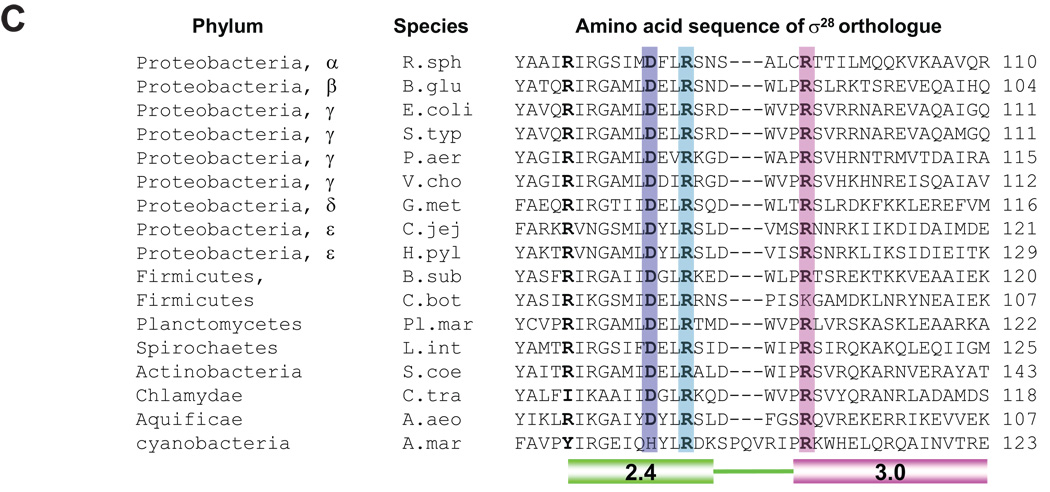
Figure 7. Structural model of recognition of the −10 region of promoters by σ28 and conservation of base-specific promoter recognitions among σ28 orthologues.
A. Comparison of the recognition of the −10 region of promoters by σ70 and σ28. Amino acid sequences of Region 2.3, 2.4 and 3.0 of σ70, σA and σ28 are shown. The −10 consensus promoter sequences for each σ is shown above or below the amino acid sequences. Arrows indicate contacts suggested by the previous studies for σ70 and in this study for σ28.
B. Shown is the structure of σA Regions 2.1–3.0 and the −10 element region of the fork junction promoter DNA from the T. aquaticus holoenzyme/fork-junction promoter DNA complex (Murakami et al., 2002). The rest of the protein and DNA are not shown. The σA Region 2.4 is colored green and Region 3.0 is magenta. Most of the 3.0 helix is transparent for clarity. The positions corresponding to residues of σ28 that make base-specific contacts with the promoter are shown as α-carbon spheres, and color-coded along with the corresponding DNA base-pair: D81 (R264 in T. aquaticus σA)/−11GC, blue; R84 (A267)/−12CG, cyan; and R91 (V277)/−13CG/–14GC, purple. This figure was prepared using PyMol (http://pymol.sourceforge.net/).
C. Conservation of amino acid residues involved in base-specific recognition of the −10 region of σ28 promoter among σ28 orthologues. Whole amino acid sequences were aligned using ClustalW and sequences from Regions 2.4 to 3.0 are shown. Residues involved in base-specific recognition are denoted by color shading. Residues homologous to R74 of E. coli σ28 are in bold. R. sph, Rhodobacter sphaeroides; B. glu, Burkholderia glumae; E. coli, Escherichia coli; S. typ, Salmonella typhimurium; P. aer, Pseudomonas aeruginosa; V. cho, Vibrio cholerae; G. met, Geobacter metallireducens; C. jej, Campylobacter jejuni; H. pyl, Helicobacter pylori; B. sub, Bacillus subtilis; C. bot, Clostridium botulinum; Pl. mar, Planctomyces maris; L. int, Leptospira interrogans; S. coe, Streptomyces coelicolor; C. tra, Chlamydia trachomatis; A. aeo, Aquifex aeolicus; A. mar, Acaryochloris marina.