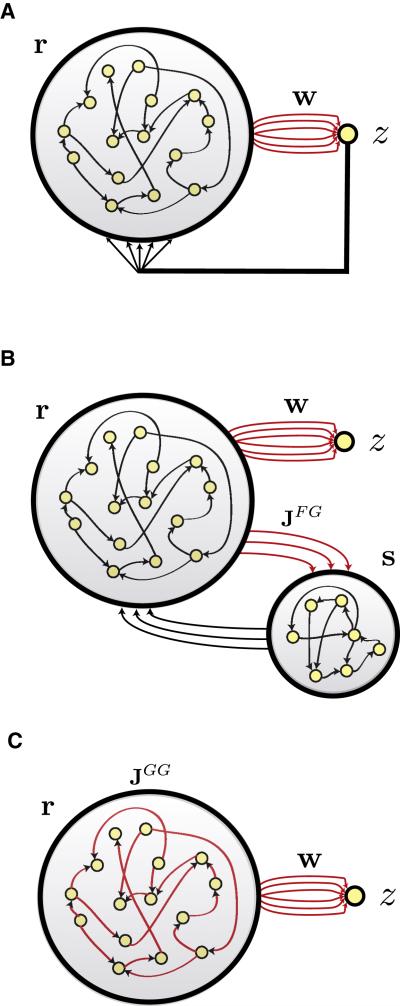
Figure 1.
Network architectures. In all three cases, a recurrent generator network with firing rates r drives a linear readout unit with output z through weights w (red) that are modified during training. Only connections shown in red are subject to modification. A) Feedback to the generator network (large network circle) is provided by the readout unit. B) Feedback to the generator network is provided by a separate feedback network (smaller network circle). Neurons of the feedback network are recurrently connected and receive input from the generator network through synapses of strength JFG (red), which are modified during training. C) A network with no external feedback. Instead, feedback is generated within the network and modified by applying FORCE learning to the synapses with strengths JGG internal to the network (red).