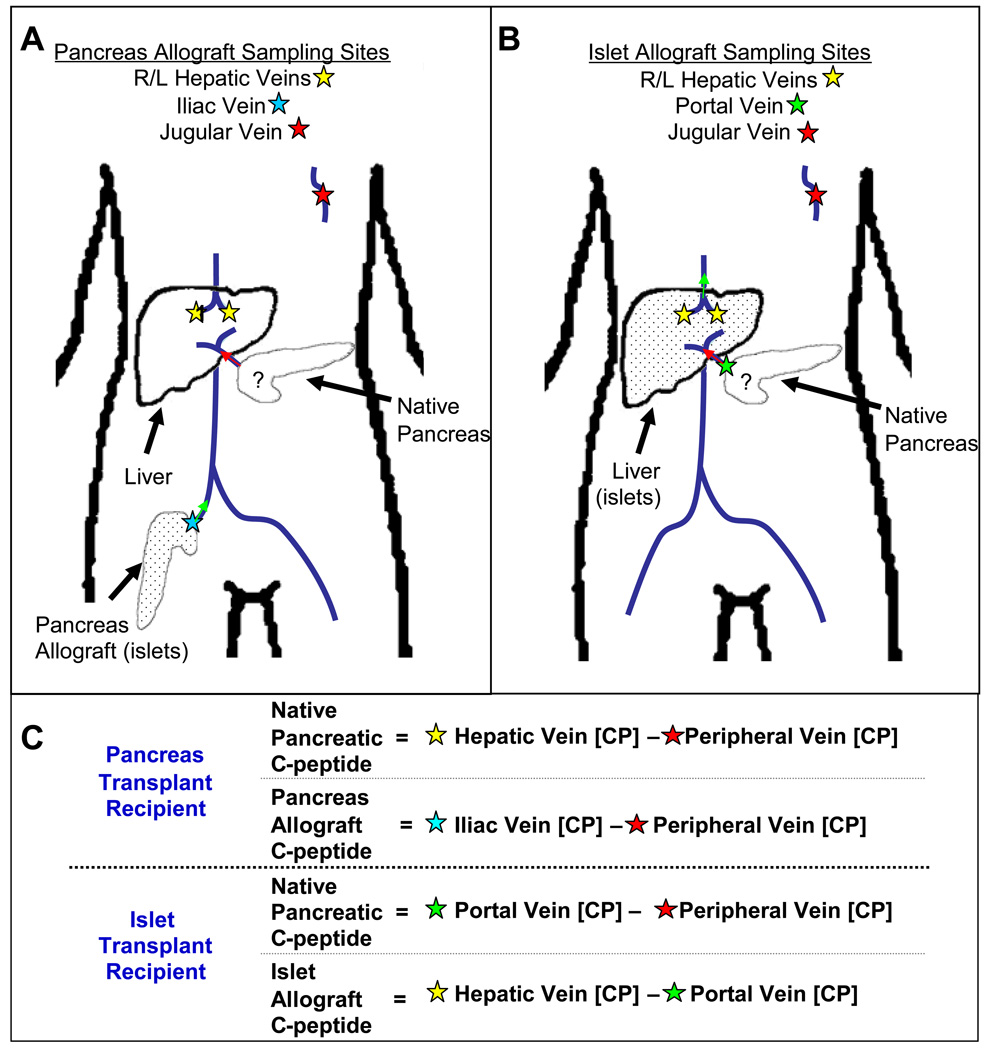
Figure 1.
Location of venous cannulas used for SAS and interpretation with transplanted beta cells represented by dots. In the whole pancreas transplant subjects, cannulas were placed in the hepatic, iliac, and jugular veins. Arginine stimulates both pancreata simultaneously. (A) Any C-peptide produced by the native pancreas is detected in the hepatic veins (yellow stars) before the C-peptide from the transplanted organ re-circulates (which will be detected by the jugular cannula). (B) In the case of islet transplant subjects, C-peptide found in the portal vein (green star) can be compared to the peripheral vein. Any early increase in the portal vein can be attributed to native pancreatic C-peptide production. (C) A mathematical representation to interpret the various sampling sites ([CP] = C-Peptide concentration).