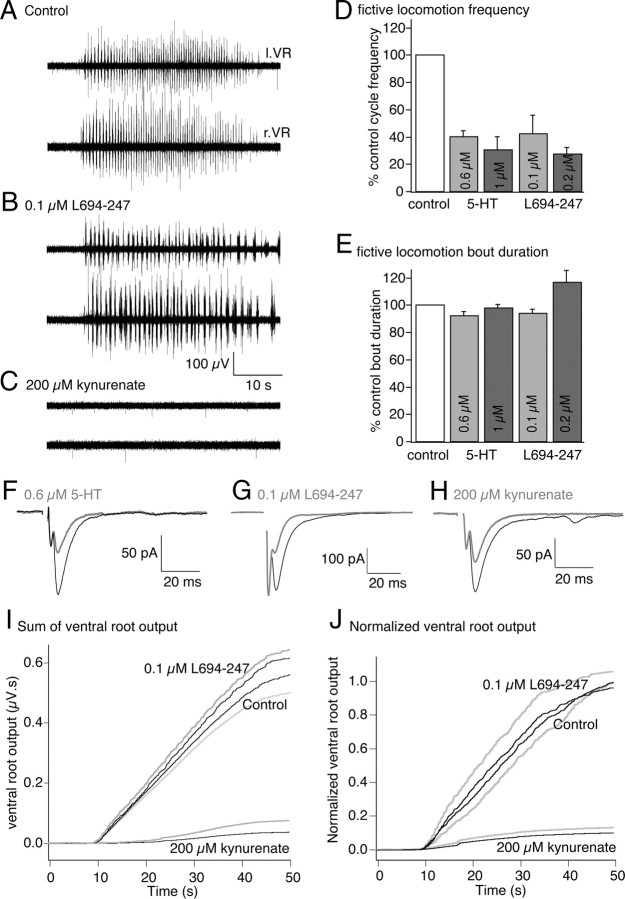
Figure 3.
5-HT1B/1D receptors reduce brainstem-activated CPG cycle frequency. A, Fictive locomotion was activated by glutamate microinjection to the MLR as for Figure 1 and recorded from pairs of ventral roots in the spinal cord. B, Application of the 5-HT1B/1D receptor agonist L694-247 (0.1 μm) to the spinal cord compartment reduced the locomotor cycle frequency but did not alter the total bout duration. C, Application of kynurenate (200 μm) to the spinal cord compartment abolished ventral root activity from the spinal cord in response to glutamate microinjection to the MLR. D, Data normalized from all preparations to show mean effects of 5-HT (from Fig. 1) and L694-247 on spinal fictive locomotion cycle frequency. Both reduced the frequency dose-dependently. E, In contrast, neither 5-HT nor L694-247 modified the total bout duration after glutamate microinjection to the MLR. Error bars indicate SEM. F–H, A comparison of the effects of 5-HT (0.6 μm), L694-247 (0.1 μm), and kynurenate (200 μm) on synaptic transmission (gray compared with black controls) mediated between paired reticulospinal axons and postsynaptic ventral horn neurons stimulated every 15 s. These agonists at these doses gave rather similar inhibitory effects on EPSCs. I, Summed absolute ventral root activity (microvolts · second) is plotted against time during the MLR evoked fictive locomotion bout. Activity was measured in three sequential locomotor bouts activated at 5 min intervals in control, in L694-247 (0.1 μm) and kynurenate (200 μm) for the preparation shown in A–C (black, mean of 3 bouts; gray, SEM for L694-247 above the mean trace and for control below the mean trace; for kynurenate SEM, gray trace above the mean trace in black). J, Normalized summed ventral root activity from all preparations (n = 5) in which L694-247 (0.1 μm) was applied (black shows mean of all preparations, SEM in gray, similarly to I).