Figure 8.
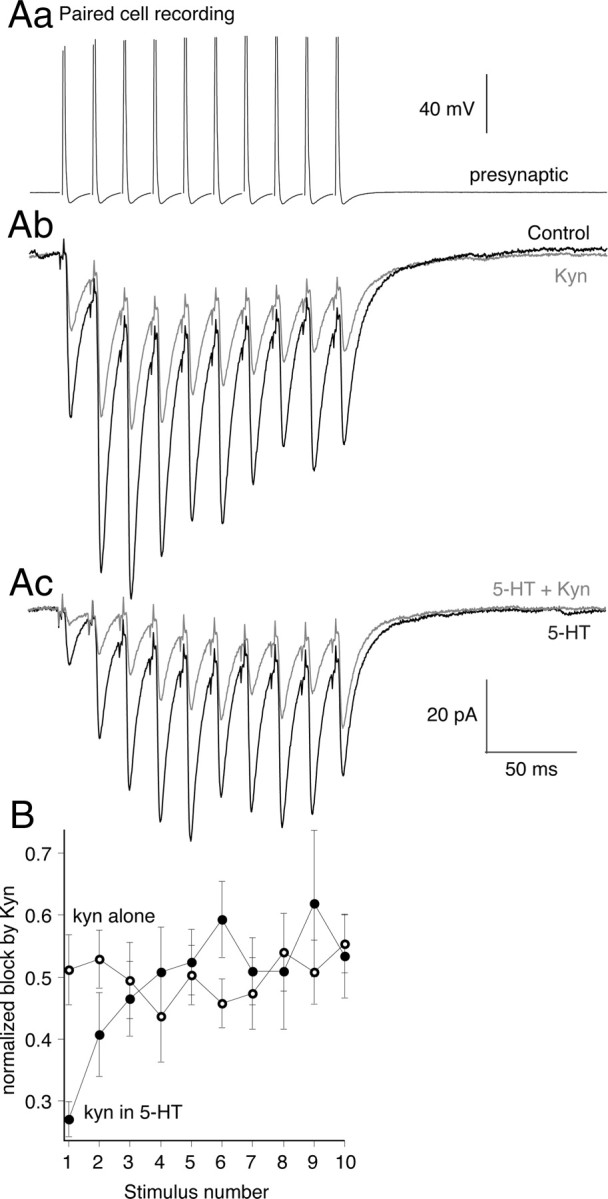
5-HT lowers evoked cleft glutamate concentrations at the start of train stimuli but not at the end. A, To probe glutamate concentration, paired recordings were made. Presynaptic action potentials (Aa) (10 at 50 Hz) evoked EPSCs (Ab) in control (black). Kynurenate (200 μm; gray) reduced EPSC amplitudes throughout the train. Ac, 5-HT (600 nm) reduced EPSC amplitudes at the start of the train but not the end (compare black trace in Ab to black trace in Ac). In 5-HT, kynurenate (200 μm; gray) was more effective at inhibiting EPSCs at the start of the train than the end. B, Graphs comparing the efficacy of kynurenate at blocking EPSCs throughout the stimulus train. In 5-HT (filled circles; n = 9), kynurenate was more effective at inhibiting the early EPSCs in 5-HT compared with control (open circles; n = 3). Error bars indicate SEM.
