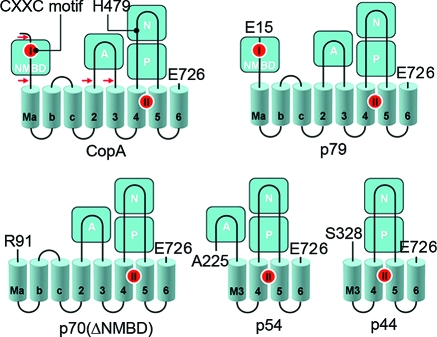
Figure 1.
Folding diagram of the T. maritima CopA sequence. The full-length sequence comprises 726 amino acids, including an N-terminal metal binding domain (NMBD), followed by four closely spaced transmembrane segments (Ma, Mb, Mc, and M2) and an extramembranous A domain. The sequence continues with two (M3 and M4) transmembrane segments, a large extramembranous region, including the N and P domains, and two closely spaced (M5 and M6) transmembrane segments at the carboxyl terminus. Two distinct copper binding sites are colored red on the NMBD and at the transmembrane site (TMBS). On the basis of partial sequence homology with other cation transport ATPases, assignments are made to the actuator domain (A) and the nucleotide binding domain (N) interspaced within the phosphorylation domain (P) sequence where D445 undergoes phosphorylation. The locations of two mutations, in the NMBD (double mutation of C17A and C20A termed the CxxC mutant) and the N domain (H479Q), are indicated in the diagram. The fragments resulting from papain cleavage of the 14 N-terminal residues at the N-terminal end to E15, at the NMBD−Ma link (N-terminal end to R91), at the M2−A domain link (N-terminal end to A225), or at the A domain−M3 link (N-terminal end to S328) are also shown. The arrows point to the cleavage sites. The peptide fragments were identified by amino acid sequencing (38).