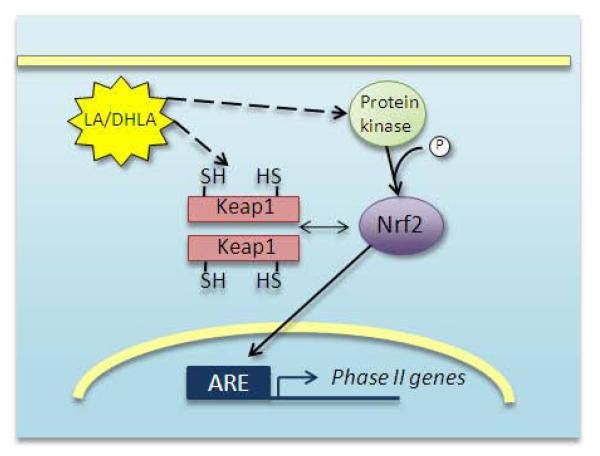
Figure 3.
Proposed action of LA for induction of Phase II genes through Nrf2-mediated transcription.
LA may oxidize critical thiols on the Keap1 dimer to halt Nrf2 degradation, and to prevent Keap1 from binding newly synthesized Nrf2. LA may also activate protein kinase signaling pathways that cause phosphorylation of Nrf2 on Ser40. This is the event that allows it to dissociate from Keap1 [68, 69]. Nrf2 can then localize to the nucleus and bind to the ARE, promoting transcription of genes for the Phase II detoxification response.