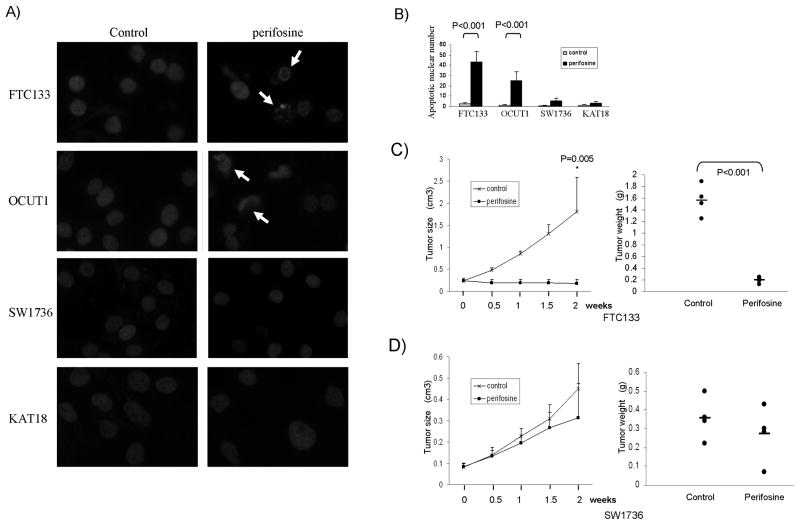
Figure 5. Genetic-selective induction of thyroid cancer cell apoptosis and inhibition of the xenograft thyroid tumor growth by the Akt inhibitor perifosine.
A) Representative morphology of cell nuclei after treatment with or without perifosine. Cells were treated with 5 μM perifosine for 48 h and apoptotic cells were determined by Hoechst 33342 staining. Cells were observed under a fluorescent microscope and selective apoptotic nuclei are indicated with arrows, showing chromatin margination, condensation and fragmentation, which are characteristics of apoptosis. B) Quantitation of the number of apoptotic cells by examining 500 cells under a fluorescent microscope for each sample. C) Effects of perifosine on the growth of xenograft tumor derived from FTC133 cells. Left panel shows the time course of tumor growth, measured as the average tumor volume in each group at the indicated time of treatment with vehicle (PBS) or perifosine, 25 mg/kg/day peritoneally. Each time point represents the average ± SD of the values obtained from 4 mice in each group. Right panel shows FTC133-derived tumor weights from the 4 individual mice in each group after a 2-week treatment. Animals were finally sacrificed and xenograft tumors were surgically removed and weighted. The average weight of the tumors from each group is indicated with a short horizontal bar. P values were obtained by Independent-sample T test. D) Effects of perifosine on the growth of SW1736-derived xenograft tumor. The experimental procedures were identical as described for FTC133 cell-derived tumors.