Fig. 3.
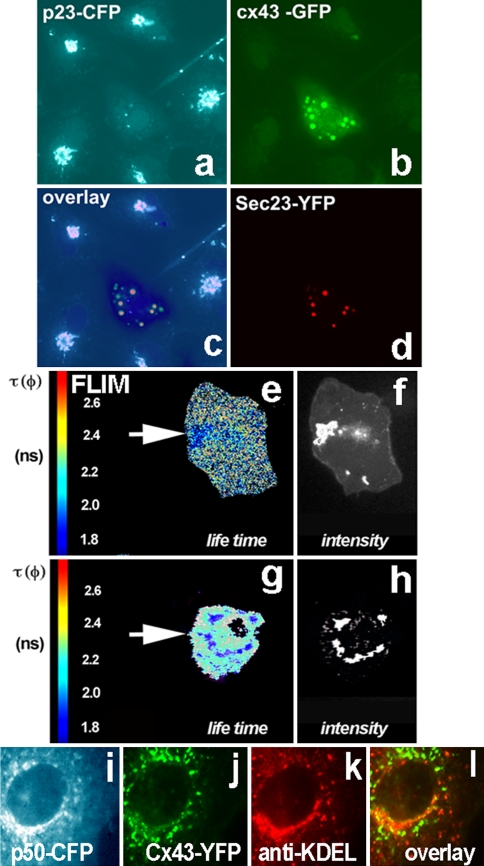
Oligomerization of Cx43 resolved in living cells using FRET-FLIM analysis. ER-to-Golgi transport of oligomerized Cx43 requires COPII and functional dynein motor complex. a p23-CFP stably expressed in Vero cells shows a typical Golgi pattern. Such cells were used for further transfection with Cx43-GFP, Sar1H79G and Sec23-YFP (a–d). The cell in the center (a) expresses all four constructs. b Cx43 is blocked in ER exit sites by Sar1H79G which also blocks p23 transport from the ER and thus prevents its Golgi accumulation (middle cell, a). Cx43 co-localizes with the COPII component Sec23-YFP (d). c Composite overlay of three channels: CFP, GFP and YFP. The fluorescence of the three channels was resolved by linear signal unmixing on the FV1000 confocal microscope. The overlay shows that in Sar1H79G expressing cells Cx43-GFP colocalizes with Sec23-YFP in ERES (resolved by EM in Fig. 2h), while the Golgi protein p23-CFP cannot be detected in the Golgi and is dispersed in the ER membrane. e–h Fluorescence Life Time Microscopy (FLIM) measurements in Vero cells co-expressing the Cx43-CFP/Cx43-YFP FRET pair. e Control cells (expressing no Sar1H79G) co-transfected with the donor/acceptor pair Cx43-CFP and Cx43-YFP show accumulation of both fluorescence signals in the Golgi region. Analysis of the distribution of lifetime (τ, given in nanoseconds) in the Golgi region reveals a strong decrease of τ. Lifetime was diminished from 2.5 to 1.9 ns as a result of FRET induced by close proximity of donor/acceptor proteins, due to oligomerization and segregation of connexins. f Wide-field microscopy image confirming strong accumulation of Cx43-FP in the Golgi region. g, h In cells co-transfected with the Cx43-CFP/Cx43-YFP donor/acceptor pair and Sar1H79G, Cx43-FP fails to arrive to the Golgi and instead appears in perinuclear dots corresponding to ERES (for comparison see EM images of ERES in Fig. 2h). h The Cx43-FP labeled perinuclear structures display a similar decrease of fluorescence lifetime (2.3–1.8 ns) as those seen in the control Golgi region (g), as a result of FRET. i–l ER–to-Golgi traffic of Cx43 utilizes the microtubule-based, minus-end directed dynein motor complex. i Overexpression of p50-CFP, the dynamitin subunit of the dynein/dynactin complex, blocks ER-to-Golgi transport of Cx43-YFP, (j); in such cells Cx43 is unable to enter the cis/medial-Golgi detected with antibodies against KDEL-receptor (k). The overlay (l) shows absence of colocalization for Cx43 with the cis/medial-Golgi marker KDEL-receptor