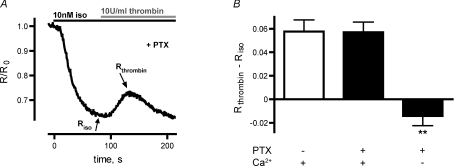
Figure 2. Thrombin-induced decrease of cAMP levels was insensitive to PTX and dependent on elevation of [Ca2+]i.
A, a representative FRET experiment shows a thrombin-mediated increase in FRET despite PTX treatment to prevent Gi activation. Riso and Rthrombin mark the minimal FRET ratio after isoproterenol stimulation and the FRET ratio about 30 s after thrombin application, respectively. B, the thrombin-induced increase of the ratiometric FRET signal, defined by Rthrombin–Riso, of PTX-incubated cells was similar to that under control conditions (n= 9). However, Rthrombin–Riso was reduced in PTX-treated HUVECs, that were measured in EGTA-buffered external solution without Ca2+ (**P < 0.01).