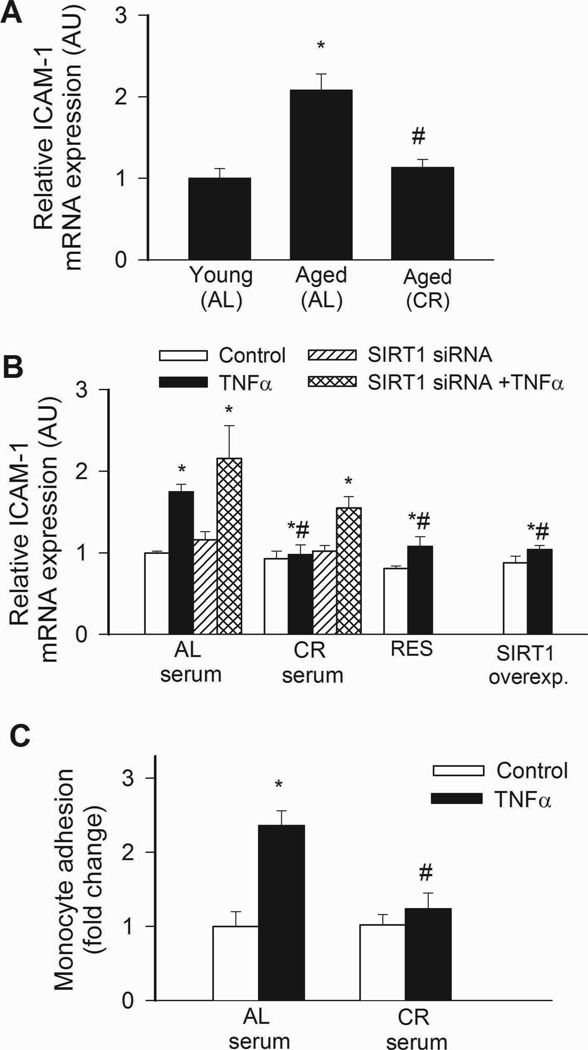
Figure 5.
A: Expression of ICAM-1 mRNA in arteries of young and aged AL fed and aged CR F344 rats. Analysis of mRNA expression was performed by real-time QRT-PCR. β-actin was used for normalization. *P<0. 05 vs. young, #P<0. 05 vs. aged AL. Data are mean ± S. E. M. (n=5 for each group). B: In CAECs cultured in the presence of AL sera TNFα (10 ng/mL) significantly increased ICAM-1 expression (*P<0. 05 vs. no TNFα). By contrast, treatment with CR serum significantly (#P<0. 05 vs. AL serum treated) attenuated TNFα-induced ICAM-1 expression. Knockdown of SIRT1 (siRNA) significantly increased ICAM both in CR sera-treated activated CAECs, decreasing the difference between the two groups ($P<0. 05 vs. TNFα). Resveratrol treatment or overexpression of SIRT1 also significantly attenuated ICAM-1 expression in activated CAECs mimicking the effects of CR serum treatment. Data are mean ± S.E.M. (n=5 in each group). C: Results of monocyte adhesion assay (see Methods). In CAECs cultured in the presence of AL sera TNFα (10 ng/mL) significantly increased the adhesion of fluorescently labeled PMA-stimulated THP-1 monocytic cells. By contrast, treatment with CR serum significantly (#P<0. 05 vs. AL serum treated) attenuated TNFα-induced monocyte adhesiveness.