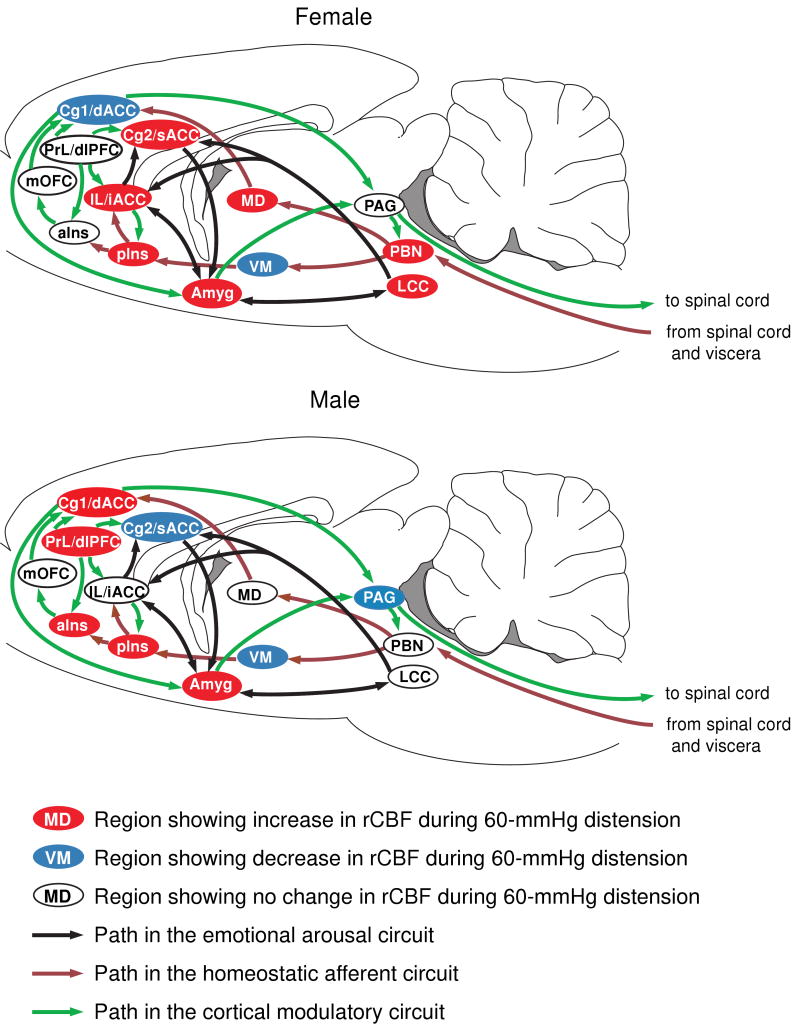
Figure 3. Sex differences in activation of the homeostatic afferent, emotional-arousal, and cortical modulatory networks in response to noxious visceral stimulation.
Regions are highlighted as showing significant increases (red), decreases (blue) or no significant change (white) in regional cerebral blood flow during 60-mmHg CRD. Abbreviations: aIns (anterior insula), Cg1 (cingulate cortex, area 1, BA24b [49]), Cg2 (cingulate cortex, area 2, BA24a [49]), dACC (dorsal anterior cingulate cortex in human), dlPFC (dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in human), iACC (infragenual anterior cingulate cortex in human), IL (infralimbic cortex, BA25 [49]), LCC (locus coeruleus complex), MD (mediodorsal thalamic nucleus), mOFC (medial orbital frontal cortex), PAG (periaqueductal gray), PBN (parabrachial nucleus), pIns (mid/posterior insula), PrL (prelimbic cortex, BA32 [49]), sACC (supragenual anterior cingulate cortex in human), VM (ventromedial thalamic nucleus). Rat brain atlas figures were reproduced with modification from Paxinos and Watson [34] with permission.