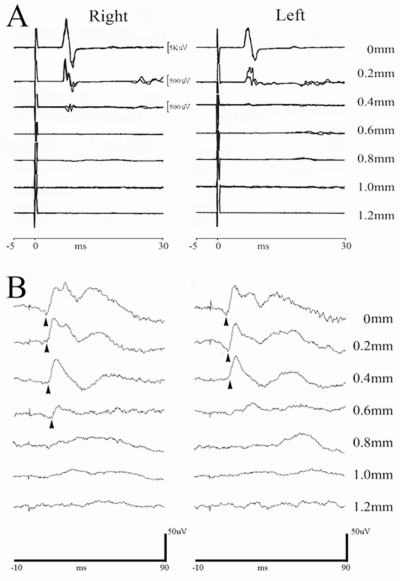
FIG. 6.
Transcranial magnetic motor evoked potentials (tcMMEPs) and somatosensory evoked potentials (SSEPs) could be recorded in all animals before surgery. (A) Representative tcMMEP waveforms of a normal animal (displacement = 0 mm) are compared to responses following graded spinal cord injury (SCI). Responses are very sensitive to injury severity (displacement > 0.2 mm). (B) SSEPs were recorded in all rats using low-intensity electrical stimulation to the posterior tibial nerve (PTN). Representative waveforms of the responses show deterioration after spinal cord contusion. Compared with the uninjured spinal cord (displacement = 0 mm), the P1 latency (arrowhead) was longer in all injury groups with a response (p < 0.01). A decreased amplitude was noted in the 0.6-mm displacement group (p = 0.058; n = 5–6/group).