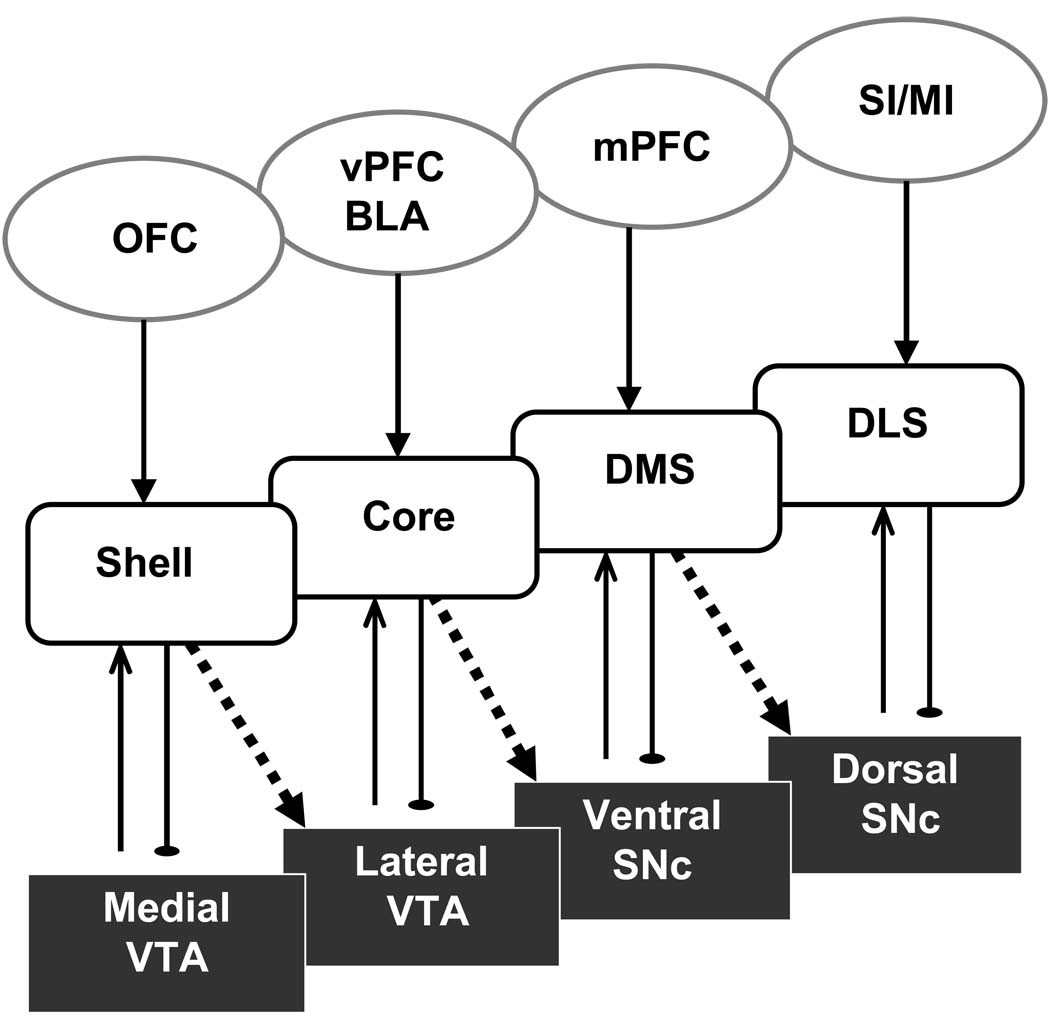
Figure 2.
The cortico-basal ganglia networks
An illustration of the major corticostriatal projections and dopaminergic projections in terms of the four major cortico-basal ganglia networks and their corresponding behavioral functions. Pallidal, thalamic, and other structures have been omitted for the sake of clarity. Emphasis is placed on the spiraling midbrain-striatum-midbrain projections, which allows information to be propagated forward in a hierarchical manner. Note that this is only one possible neural implementation; interactions via different thalamo-cortico-thalamic projections are also possible (Haber, 2003). BLA, basolateral amygdale complex; mPFC, medial prefrontal cortex; vPFC, ventral prefrontal cortex; SI/MI, primary sensory and motor cortices; DLS, dorsolateral striatum; DMS, dorsomedial striatum; shell, nucleus accumbens shell; core, nucleus accumbens core.