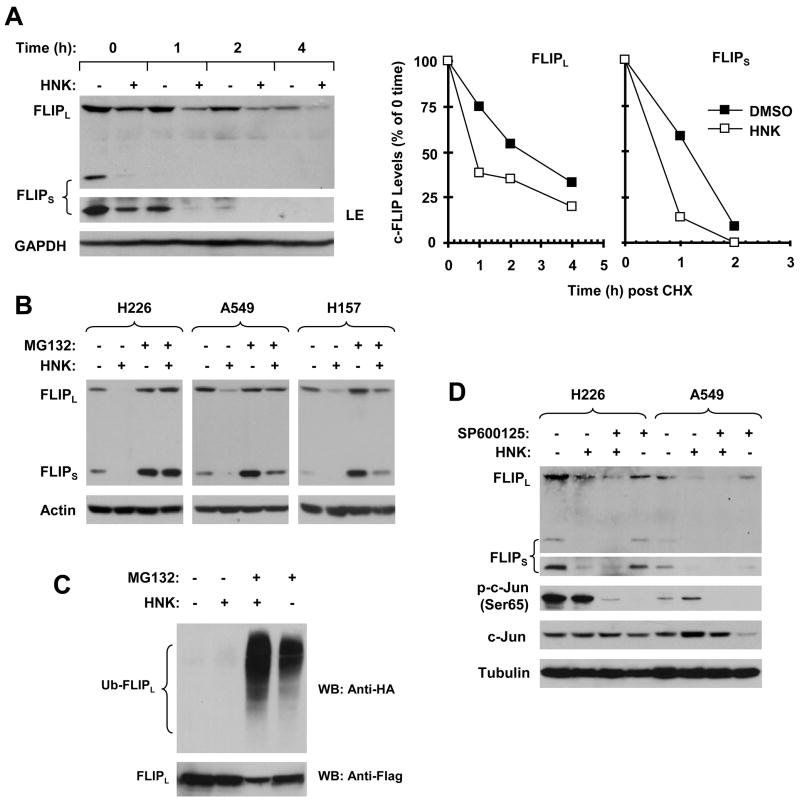
Fig. 4. HNK modulates c-FLIP levels through ubiquitin/proteasome-mediated protein degradation (A–C) independent of JNK (D).
A, H226 cells were treated with DMSO or 30 μM HNK for 5 h. The cells were then washed with PBS 3 times and refed with fresh medium containing 10 ug/ml CHX. At the indicated times, the cells were harvested for preparation of whole-cell protein lysates and subsequent Western blot analysis. Protein levels were quantitated with NIH Image J software (Bethesda, MA) and were normalized to GAPGH. The results were plotted as the relative c-FLIP levels compared to those at the time 0 of CHX treatment (right panel). LE, longer exposure. B, The given cell lines were pretreated with 20 μM MG132 for 30 minutes prior to the addition of HNK (30 μM for H226 and A549; 25 μM for H157). After co-treatment for 4 h, the cells were harvested for preparation of whole-cell protein lysates and subsequent Western blot analysis. C, H157-FLIPL-21 cells which stably express ectopic flag-FLIPL were transfected with HA-ubiquitin plasmid using FuGENE 6 transfection reagent for 24 h. The cells were then pretreated with 20 μM MG132 for 30 minutes and then co-treated with 25 μM HNK for 4 h. Whole-cell protein lysates were then prepared for immunoprecipitation using anti-Flag antibody followed by Western blotting (WB) using anti-HA antibody for detection of ubiquitinated FLIPL (Ub-FLIPL) and anti-Flag antibody for detection of ectopic FLIPL. D, The indicated cell lines were pretreated with 20 μM SP600125 for 30 min and then co-treated with 30 μM HNK for another 6 h. The cells were then subjected to preparation of whole-cell protein lysates and subsequent Western blot analysis for detection of the indicated proteins.