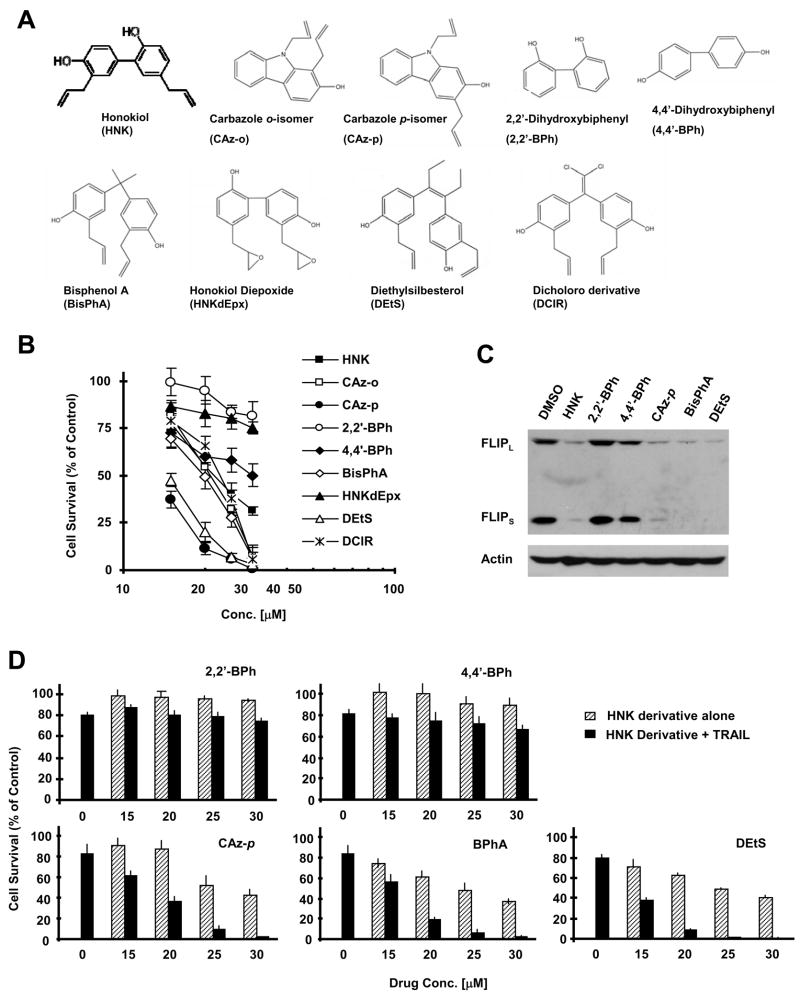
Fig. 6. Comparing the effects of HNK derivatives (A) on cell growth (B), downregulation of c-FLIP (C) and augmentation of TRAIL-induced apoptosis (D).
A, Chemical structures of HNK derivatives. B, H226 cells were seeded in 96-well plates and treated with the indicated concentrations of HNK. After 3 days, the cells were subjected to the SRB assay for measurement of cell survival. C, H226 cells were treated with 30 μM of the indicated HNK derivatives for 4 h and then subjected to preparation of whole-cell protein lysates and subsequent Western blot analysis. D, H226 cells were seeded in 96-well plates and treated with the indicated concentrations of HNK derivative alone, 20 ng/ml TRAIL alone, or their combination. After 24 h, the cells were subjected to the SRB assay for measurement of cell survival. Data in B and D are the means of four replicate determinations. Bars; ± SDs.