Fig. 1.
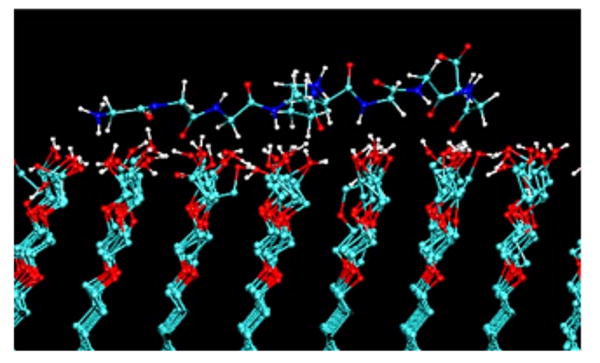
A snap shot from a molecular dynamics simulation of a G4-K-G4 peptide over an oligo(ethylene-oxide)-SAM surface [OEG, functional group structure: (-O-CH2-CH2)2-OH)] using the default gromacs force field parameters (Ref. 138). The peptide strongly adsorbed to the OEG surface via a combination of hydrogen bonds with the OH groups at the end of the OEG chains and hydrophobic interactions between CH2 groups of the peptide and the ethylene segments of the OEG chains. Experimental studies show this type of surface to be very nonadsorbing for peptides and proteins (Ref. 78) This simulation thus demonstrates an example where the force field parameters are not properly tuned to represent realistic adsorption behavior. Adapted from Ref. 76; used with permission.
