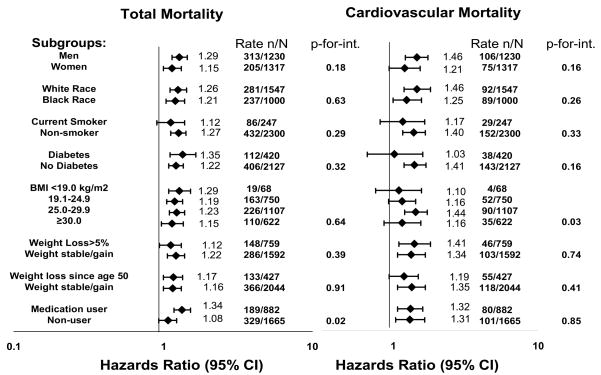
Figure.
The association between adiponectin (per SD) and total and cardiovascular mortality by subgroup after adjustment for age, sex, race, study site, smoking, hypertension, diabetes, prevalent coronary heart disease, LDL-cholesterol, cystatin C, estrogen use, BMI, abdominal visceral fat, thigh intermuscular fat, thigh muscle area, HDL-cholesterol, insulin, and triglycerides (without adjustment for the subgroup variable of interest). We present p-for-interaction for each subgroup. *Medication use refers to any participant taking a medication that increases adiponectin concentrations: insulin, a thiazolidinedione, an angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor, an angiotensin II receptor blocker, a beta blocker, or a statin medication. Those not on any of these medications are termed as medication non-user.