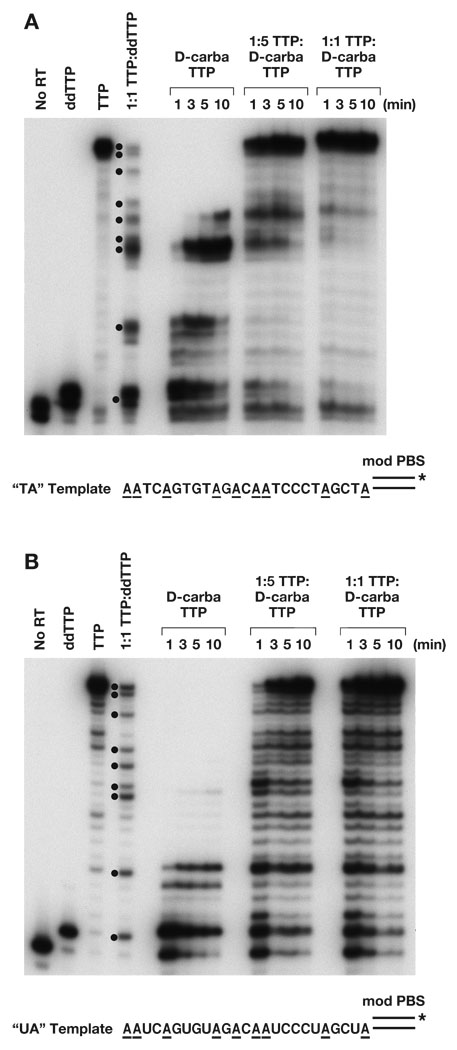
Figure 2.
Inhibition of DNA synthesis by D-carba T-TP. As described in Experimental, the primer was 5′ end-labeled, then annealed to either a DNA template (2A) or an RNA template (2B). The “No RT” lane shows the size of the starting primer. All reactions had 10.0 µM each of dCTP, dGTP, dATP, and the indicated TTP or T-TP analog. The “ddTTP” lane shows the primer with the addition of a single ddTTP residue (N + 1), while the “TTP” lane shows the primer extended to the end the template (full-length product). The 1:1 TTP:ddTTP had a mixture of 5.0 µM TTP and 5.0 µM ddTTP in the reaction. Because ddT-TP is an immediate chain terminator, DNA synthesis carried out with this mixture generates products corresponding to all of the sites at which a TTP or TTP analog can be incorporated. The positions at which the addition of ddTTP terminated DNA synthesis are indicated by dots. The reactions were carried out either with 10.0 µM D-carba T-TP (no TTP present) or with different ratios of TTP:D-carba T-TP (1:5 or 1:1) where the final concentration totaled 10.0 µM. The reactions were incubated at 37° for the indicated length of time and the products fractionated by gel electrophoresis. The unusual pause site discussed in the text for an RNA template is marked with a star. The sequence of the template extension is shown below the reactions, and the positions of all “A” residues are highlighted