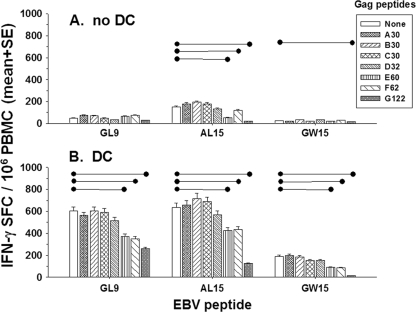
FIG. 3.
Larger pools of HIV-1 peptides result in lower IFN-γ production by EBV-specific T cells. HLA A*0201-restricted EBV GL9 and its N (AL15)- and C (GW15)-terminal extensions (5 μg/ml) were mixed with different sizes of HIV-1 Gag peptide pools (5 μg/ml), with and without DC, in the ELISPOT assay. Data are mean SFC ± standard errors from three HIV-1-negative subjects. The data show that without DC (A) there was no difference in GL9 peptide-specific IFN-γ production when it was mixed with any of the Gag peptide pools (P = NS). There were decreases in AL15-specific IFN-γ production when this peptide was mixed with either the Gag 60/62 pool (•—•, P < 0.05) or the Gag G122 pool (•—•, P < 0.001), and there were decreases in GW15-specific IFN-γ production when this peptide was mixed with the Gag G122 peptide pool (P < 0.05). When used with DC (B), there were significant decreases in GL9, AL15, and GW15 peptide-specific IFN-γ production when the peptides were mixed with either the Gag 60/62 pool or the Gag G122 pool (P < 0.01).