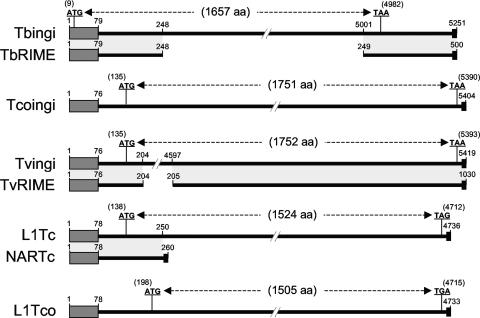
FIG. 2.
Schematic representation and comparison of potentially active autonomous and nonautonomous families of retroposons belonging to the ingi clade. The schematic maps are based on the consensus sequences generated from alignments of the Tbingi and TbRIME (T. brucei), Tcoingi and L1Tco (T. congolense), Tvingi and TvRIME (T. vivax), and L1Tc and NARTc (T. cruzi) retroposon sequences. The autonomous Tbingi, Tcoingi, Tvingi, and L1Tc consensus sequences contain a single long open reading frame coding for a multifunctional protein containing the endonuclease, RT, RNase H, and leucine zipper domains (the number of amino acids [aa] composing the encoded protein is indicated in parentheses). For L1Tco, four frameshifts were introduced into the consensus sequence to restore the putative coding sequence. The positions of the start and stop codons are indicated. Matches between autonomous and nonautonomous (TbRIME, TvRIME, and NARTc) retroposons are shown by light-gray boxes. The black boxes at the ends of both maps represent the poly(dA) terminal sequence. The N-terminal conserved motif, representing the trypanosomatid retroposon signature, is indicated by a dark-gray box.