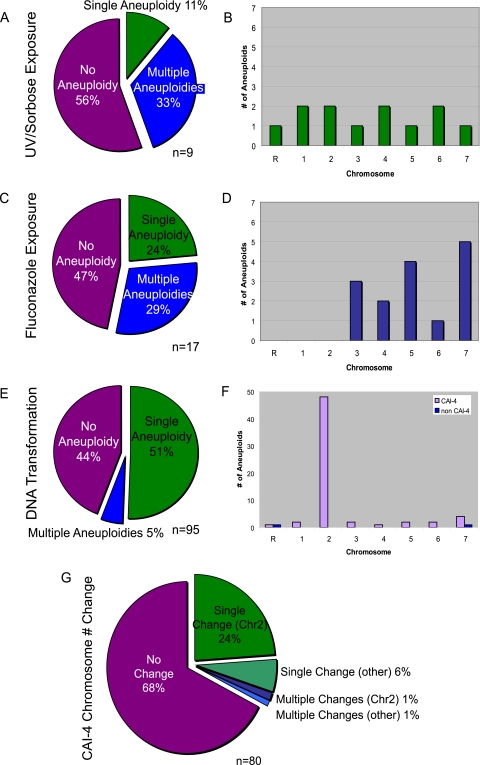
FIG. 3.
Aneuploidy is common in strains treated with UV/sorbose or fluconazole and in strains transformed with DNA. The proportions of strains from each experiment type (UV/sorbose exposure, fluconazole exposure, DNA transformation) that exhibit no aneuploidy, a single aneuploid chromosome, and multiple aneuploid chromosomes (A, C, and E) and of chromosomes that became aneuploid (B, D, and F) are shown. Because CAI-4 was aneuploid prior to transformation, genome instability is indicated as a change in chromosome copy number, and this change frequently involved the aneuploid chromosome Chr2 (G).