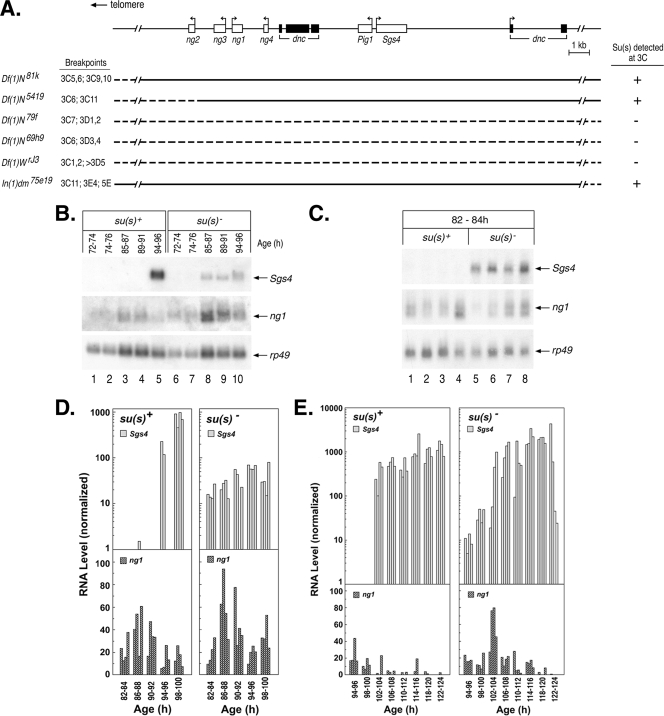
FIG. 3.
Su(s) prevents aberrant temporal accumulation of wild-type Sgs4 and ng1 transcripts. (A) Schematic map of genes in the 3C10 to 3C11 region. Immunofluorescence analysis of deficiency stocks confirmed that Su(s) localization requires sequences within this genomic interval. Dashed lines indicate sequences deleted in each deficiency stock. (B, C) Representative developmental Northern blots of total RNA isolated from various stages (h after egg laying) of su(s)+ and su(s)− larvae. Probes used are shown on the right. Each lane contains RNA from multiple larvae (B) or a single larva (C). (D, E) Graphical representation of developmental Northern blots of RNA from individual larvae at various times during the early (D) and late (E) third-instar stages. Sgs4 and ng1 RNA signals were normalized to rp49. The data shown in panel C are included in panel D. The development of both the su(s)+ and su(s)− larvae in the experiment for which the results are shown in panel E was delayed relative to that of the larvae in the experiments for which the results are shown in panels B and D, i.e., Sgs4 induction occurred at 102 to 104 h instead of 94 to 96 h. This effect was probably related to the batch of larval food used in this experiment.