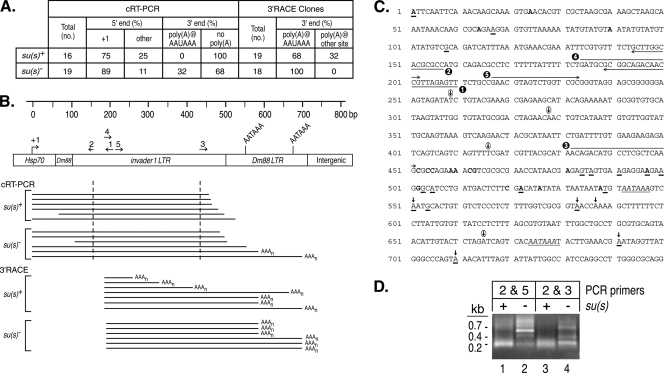
FIG. 5.
cRT-PCR and 3′ RACE experiments suggest that Su(s) promotes the degradation of αβ RNAs. (A) Summary of αβ cDNA clone sequence data. The RNA used in these experiments was from su(s)+ and su(s)− flies heat shocked at 32°C. (B) Schematic map of a portion of an αγ element. Numbered arrows above the map indicate the primers used in this analysis. Horizontal lines beneath the map indicate the types of cDNAs recovered in these experiments. The cDNA clones obtained by cRT-PCR contained sequences upstream and downstream of the dashed vertical lines. Poly(A) tails at the 3′ ends are indicated by AAAn. (C) Sequences of the first 750 bp of an αγ element. Transcription starts at +1. Primers used for cRT-PCR and 3′ RACE are indicated by the numbered arrows. Polyadenylation signals AATAAA are italicized and underlined. Bold vertical arrows above the sequences indicate canonical polyadenylation sites detected in cRT-PCR and 3′ RACE experiments. Circled vertical arrows indicate unusual polyadenylation sites detected only in 3′ RACE of su(s)+ RNA. The 5′ and 3′ ends of su(s)+ cDNA clones generated by cRT-PCR are shown in bold. The 5′ ends of these cDNAs were at positions 1, 24, 64, and 90; the 3′ ends were at positions 452, 454, 455, 459, 460, 462, 463, 481, 497, 502, 520, 522, 526, and 538. The 5′ and 3′ ends of su(s)− cDNA clones obtained by cRT-PCR are underlined. The 5′ ends were at positions 1, 67, and 108; the 3′ ends were at positions 484, 486, 491, 497, 500, 503, 505, 522, 539, 551, 554, 583, 691, and 710. (D) Ethidium bromide-stained agarose gel of cRT-PCR products prior to cloning. The PCR primers used are shown in panel C. Similarly sized fragments were seen with both primer sets from the su(s)+ samples. This is probably because most of the cDNAs were amplified from RNAs with intact 5′ ends and extensively degraded 3′ ends. Thus, many cDNAs were truncated within a short distance of the downstream primer (primer 3 or 5). In contrast, longer cDNAs were amplified from su(s)− RNA.